Schistosomiasis-Microbiota Interactions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 39452777
- PMCID: PMC11510367
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13100906
Schistosomiasis-Microbiota Interactions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Schistosomiasis, a tropical disease affecting humans and animals, affected 251.4 million people in 2021. Schistosoma mansoni, S. haematobium, S. intercalatum, and S. japonicum are primary human schistosomes, causing tissue damage, granulomas, ulceration, hemorrhage, and opportunistic pathogen entry. The gut and urinary tract microbiota significantly impact a host's susceptibility to schistosomiasis, disrupting microbial balance; however, this relationship is not well understood. This systematic review and meta-analysis explores the intricate relationship between schistosomiasis and the host's microbiota, providing crucial insights into disease pathogenesis and management.
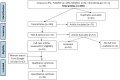
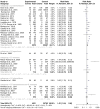
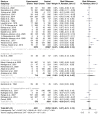
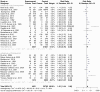
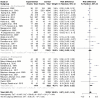
Methods: This systematic review used PRISMA guidelines to identify peer-reviewed articles on schistosomiasis and its interactions with the host microbiome, using multiple databases and Google Scholar, providing a robust dataset for analysis. The study utilized Meta-Mar v3.5.1; descriptive tests, random-effects models, and subgroups were analyzed for the interaction between Schistosomiasis and the microbiome. Forest plots, Cochran's Q test, and Higgins' inconsistency statistic (I2) were used to assess heterogeneity.
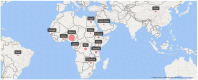
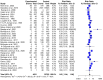
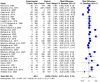
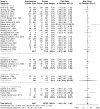
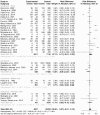
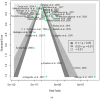
Results: The human Schistosoma species were observed to be associated with various bacterial species isolated from blood, stool, urine, sputum, skin, and vaginal or cervical samples. A meta-analysis of the interaction between schistosomiasis and the host microbiome, based on 31 studies, showed 29,784 observations and 5871 events. The pooled estimates indicated a significant association between schistosomiasis and changes in the microbiome of infected individuals. There was considerable heterogeneity with variance effect sizes (p < 0.0001). Subgroup analysis of Schistosoma species demonstrated that S. haematobium was the most significant contributor to the overall heterogeneity, accounting for 62.1% (p < 0.01). S. mansoni contributed 13.0% (p = 0.02), and the coinfection of S. haematobium and S. mansoni accounted for 16.8% of the heterogeneity (p < 0.01), contributing to the variability seen in the pooled analysis. Similarly, praziquantel treatment (RR = 1.68, 95% CI: 1.07-2.64) showed high heterogeneity (Chi2 = 71.42, df = 11, p < 0.01) and also indicated that Schistosoma infections in males (RR = 1.46, 95% CI: 0.00 to 551.30) and females (RR = 2.09, 95% CI: 0.24 to 18.31) have a higher risk of altering the host microbiome.
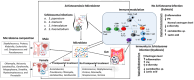
Conclusions: Schistosomiasis significantly disrupts the host microbiota across various bodily sites, leading to increased susceptibility to different bacterial taxa such as E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Mycobacterium species (M. tuberculosis and M. leprae). This disruption enables these bacteria to produce toxic metabolites, which in turn cause inflammation and facilitate the progression of disease. The impact of schistosomiasis on the vaginal microbiome underscores the necessity for gender-specific approaches to treatment and prevention. Effective management of female genital schistosomiasis (FGS) requires addressing both the parasitic infection and the resulting microbiome imbalances. Additionally, praziquantel-treated individuals have different microbiome compositions compared to individuals with no praziquantel treatment. This suggests that combining praziquantel treatment with probiotics could potentially decrease the disease severity caused by an altered microbiome.
Keywords: dysbiosis; immune modulation; microbial diversity; microbiota; schistosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Schistosomiasis Fact Sheet 2021. [(accessed on 2 April 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/details/schistosomiasis.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

