Interleukin-1 Beta rs16944 and rs1143634 and Interleukin-6 Receptor rs12083537 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Potential Predictors of COVID-19 Severity
- PMID: 39452786
- PMCID: PMC11510688
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens13100915
Interleukin-1 Beta rs16944 and rs1143634 and Interleukin-6 Receptor rs12083537 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Potential Predictors of COVID-19 Severity
Abstract
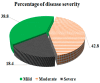
Host genetic variation has been recognized as a key predictor of diverse clinical sequelae among severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-infected patients. Insights into the link between the Interleukin-6 receptor (IL-6R) and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) genetic variation and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are crucial for developing new predictors and therapeutic targets. We aimed to investigate the association of IL-6R rs12083537, IL-1β rs16944, and IL-1β rs1143634 SNPs with the severity of COVID-19. Our study was conducted on 300 COVID-19-negative individuals (control group) and 299 COVID-19-positive cases, classified into mild, moderate, and severe subgroups. Analyses of IL-1β (rs16944, rs1143634) and IL-6R (rs12083537) SNPs' genotypes were performed using qPCR genotyping assays. The IL-1β (rs16944) CC genotype and IL-6R (rs12083537) GG genotype were substantially related to COVID-19 severity, which was also associated with comorbidities and some laboratory parameters (p < 0.001). The IL-1β (rs1143634) TT genotype was found to be protective. Likewise, the IL-1β (rs16944) CC genotype was associated with increased mortality. IL-1β rs16944 and IL-6R rs12083537 SNPs are promising potential predictors of SARS-CoV-2 disease severity. Meanwhile, the rs1143634 SNP T allele was protective against severity and mortality risk.
Keywords: COVID-19; SNPs; genotype; interleukin-1 beta; interleukin-6 receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdulla Z.A., Al-Bashir S.M., Alzoubi H., Al-Salih N.S., Aldamen A.A., Abdulazeez A.Z. The Role of Immunity in the Pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and in the Protection Generated by COVID-19 Vaccines in Different Age Groups. Pathogens. 2023;12:329. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020329. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous