Clinical Outcomes of Benzodiazepine Prescribing for People Receiving Opioid Agonist Treatment: A Systematic Review of the Evidence
- PMID: 39452808
- PMCID: PMC11511121
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmacy12050152
Clinical Outcomes of Benzodiazepine Prescribing for People Receiving Opioid Agonist Treatment: A Systematic Review of the Evidence
Abstract
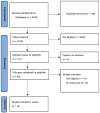
Many countries are experiencing an increased use of unregulated benzodiazepines in combination with opioids and other drugs, which contributes to drug-related harm. This descriptive review identifies and synthesises the outcomes of studies co-prescribing benzodiazepines and opioids. A systematic review was undertaken in Medline, CINAHL, PsychInfo, Embase, and the Cochrane databases covering publications from 1 January 1991 to 18 November 2021. Inclusion criteria were peer reviewed, English language studies of adults prescribed opioid agonist treatment (OAT) and a concurrent benzodiazepine, and reporting outcome data. Of the 4370 titles screened, 18 papers were included. The main outcomes identified covered all-cause mortality (ACM) (n = 5); overdose death (n = 3); retention in treatment (n = 7); and hospitalisation/emergency department encounters (n = 2). Other outcomes included QTc interval, cognitive function, illicit drug use, and mental health. The prescription of benzodiazepines alongside OAT increased the ACM by 75-90%, while evidence on overdose death was less robust but indicative of increased risk (40-334%). There was an indicative positive effect on treatment retention, with increased retention in those prescribed a benzodiazepine with OAT compared to those not prescribed or taking non-prescribed benzodiazepines. In conclusion, methodologically robust epidemiological studies found increased ACM and overdose death but possibly improved retention. However confounders (e.g., psychiatric comorbidity) exist, so a trial is recommended.
Keywords: addiction; benzodiazepine prescription; clinical decision-making; clinical outcomes; drug overdose; illicit drug use; mortality; opioid agonist treatment; opioid replacement treatment; street benzodiazepines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prescription of benzodiazepines, z-drugs, and gabapentinoids and mortality risk in people receiving opioid agonist treatment: Observational study based on the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink and Office for National Statistics death records.PLoS Med. 2019 Nov 26;16(11):e1002965. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002965. eCollection 2019 Nov. PLoS Med. 2019. PMID: 31770388 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between prescribed benzodiazepines, overdose death and buprenorphine discontinuation among people receiving buprenorphine.Addiction. 2020 May;115(5):924-932. doi: 10.1111/add.14886. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Addiction. 2020. PMID: 31916306 Free PMC article.
-
Prescribing of Opioids and Benzodiazepines Among Patients With History of Overdose.J Addict Med. 2019 Sep/Oct;13(5):396-402. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000513. J Addict Med. 2019. PMID: 30844876 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a diazepam milligram equivalency algorithm to assess benzodiazepine dose intensity in Rhode Island in 2018.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2022 Jan;28(1):58-68. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2022.28.1.58. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2022. PMID: 34949119 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiology of benzodiazepine misuse: A systematic review.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019 Jul 1;200:95-114. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2019.02.033. Epub 2019 May 7. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019. PMID: 31121495 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Essink S., Nugteren-van Lonkhuyzen J.J., van Riel A.J.H.P., Dekker D., Hondebrink L. Significant toxicity following an increase in poisonings with designer benzodiazepines in The Netherlands between 2010 and 2020. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2022;231:109244. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2021.109244. - DOI - PubMed
-
- National Records of Scotland Drug-Related Deaths in Scotland in 2021. [(accessed on 5 December 2022)];2022 Available online: https://www.nrscotland.gov.uk/files/statistics/drug-related-deaths/21/dr....
-
- Office for National Statistics Deaths Related to Drug Poisoning in England and Wales: 2022 Registrations. [(accessed on 5 December 2022)];2023 Available online: https://backup.ons.gov.uk/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2023/12/Deaths-rela....
-
- Northern Ireland Statistics and Research Agency Drug-Related and Drug-Misuse Deaths 2011–2021. [(accessed on 8 December 2022)]; Available online: https://www.nisra.gov.uk/publications/drug-related-and-drug-misuse-death....
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources