Unraveling the Omega-3 Puzzle: Navigating Challenges and Innovations for Bone Health and Healthy Aging
- PMID: 39452854
- PMCID: PMC11509197
- DOI: 10.3390/md22100446
Unraveling the Omega-3 Puzzle: Navigating Challenges and Innovations for Bone Health and Healthy Aging
Abstract
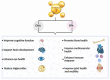
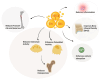
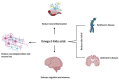
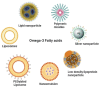
Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (ω-3 PUFAs, n-3 PUFAs), including eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), are essential polyunsaturated fats primarily obtained from fatty fish and plant-based sources. Compelling evidence from preclinical and epidemiological studies consistently suggests beneficial effects of ω-3 PUFAs on bone health and healthy aging processes. However, clinical trials have yielded mixed results, with some failing to replicate these benefits seen in preclinical models. This contraindication is mainly due to challenges such as low bioavailability, potential adverse effects with higher doses, and susceptibility to oxidation of ω-3 fatty acids, hindering their clinical effectiveness. This review comprehensively discusses recent findings from a clinical perspective, along with preclinical and epidemiological studies, emphasizing the role of ω-3 PUFAs in promoting bone health and supporting healthy aging. Additionally, it explores strategies to improve ω-3 PUFA efficacy, including nanoparticle encapsulation and incorporation of specialized pro-resolving mediators (SPM) derived from DHA and EPA, to mitigate oxidation and enhance solubility, thereby improving therapeutic potential. By consolidating evidence from various studies, this review underscores current insights and future directions in leveraging ω-3 PUFAs for therapeutic applications.
Keywords: aging; bioavailability; bone health; docosahexaenoic acid (DHA); eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); nanoparticle encapsulation; omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; specialized proresolving mediators (SPM).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials