Silver Nanoparticles in Therapeutics and Beyond: A Review of Mechanism Insights and Applications
- PMID: 39452955
- PMCID: PMC11510578
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14201618
Silver Nanoparticles in Therapeutics and Beyond: A Review of Mechanism Insights and Applications
Abstract
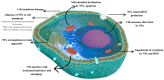
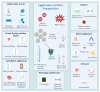
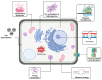
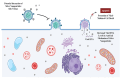
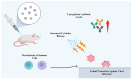
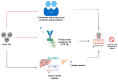
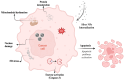
Silver nanoparticles (NPs) have become highly promising agents in the field of biomedical science, offering wide therapeutic potential due to their unique physicochemical properties. The unique characteristics of silver NPs, such as their higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, make them ideal for a variety of biological applications. They are easily processed thanks to their large surface area, strong surface plasmon resonance (SPR), stable nature, and multifunctionality. With an emphasis on the mechanisms of action, efficacy, and prospective advantages of silver NPs, this review attempts to give a thorough overview of the numerous biological applications of these particles. The utilization of silver NPs in diagnostics, such as bioimaging and biosensing, as well as their functions in therapeutic interventions such as antimicrobial therapies, cancer therapy, diabetes treatment, bone repair, and wound healing, are investigated. The underlying processes by which silver NPs exercise their effects, such as oxidative stress induction, apoptosis, and microbial cell membrane rupture, are explored. Furthermore, toxicological concerns and regulatory issues are discussed, as well as the present difficulties and restrictions related to the application of silver NPs in medicine.
Keywords: antimicrobial and anticancer activity; bioimaging and biosensor; biomedical applications; bone healing and wound repair activity; dental applications; diabetes; silver nanoparticles; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

