Introduction and Development of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrates: A Review
- PMID: 39452983
- PMCID: PMC11510290
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14201648
Introduction and Development of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) Substrates: A Review
Abstract
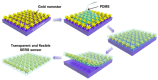
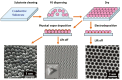
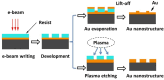
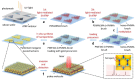
Since its discovery, the phenomenon of Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) has gradually become an important tool for analyzing the composition and structure of substances. As a trace technique that can efficiently and nondestructively detect single molecules, the application of SERS has expanded from environmental and materials science to biomedical fields. In the past decade or so, the explosive development of nanotechnology and nanomaterials has further boosted the research of SERS technology, as nanomaterial-based SERS substrates have shown good signal enhancement properties. So far, it is widely recognized that the morphology, size, composition, and stacking mode of nanomaterials have a very great influence on the strength of the substrate SERS effect. Herein, an overview of methods for the preparation of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrates is provided. Specifically, this review describes a variety of common SERS substrate preparation methods and explores the potential and promise of these methods for applications in chemical analysis and biomedical fields. By detailing the influence of different nanomaterials (e.g., metallic nanoparticles, nanowires, and nanostars) and their structural features on the SERS effect, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of SERS substrate preparation techniques.
Keywords: SERS; preparation; substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
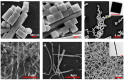
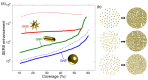
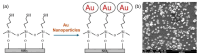
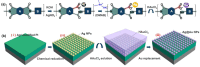
References
-
- Demming F., Jersch J., Dickmann K., Geshev P.I. Calculation of the field enhancement on laser-illuminated scanning probe tips by the boundary element method. Appl. Phys.-Sect. B-Lasers Opt. 1998;66:593–598. doi: 10.1007/s003400050441. - DOI
-
- Fredericks P.M. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy in Forensic Science. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2012.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

