Mandarin Peels-Derived Carbon Dots: A Multifaceted Fluorescent Probe for Cu(II) Detection in Tap and Drinking Water Samples
- PMID: 39453002
- PMCID: PMC11509961
- DOI: 10.3390/nano14201666
Mandarin Peels-Derived Carbon Dots: A Multifaceted Fluorescent Probe for Cu(II) Detection in Tap and Drinking Water Samples
Abstract
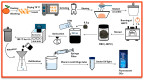
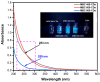
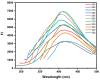
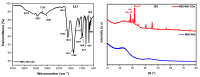
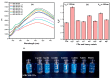
Carbon dots (CDs) derived from mandarin peel biochar (MBC) at different pyrolysis temperatures (200, 400, 600, and 800 °C) have been synthesized and characterized. This high-value transformation of waste materials into fluorescent nanoprobes for environmental monitoring represents a step forward towards a circular economy. In this itinerary, CDs produced via one-pot hydrothermal synthesis were utilized for the detection of copper (II) ions. The study looked at the spectroscopic features of biochar-derived CDs. The selectivity of CDs obtained from biochar following carbonization at 400 °C (MBC400-CDs towards various heavy metal ions resulted in considerable fluorescence quenching with copper (II) ions, showcasing their potential as selective detectors. Transmission electron microscopic (TEM) analysis validated the MBC-CDs' consistent spherical shape, with a particle size of <3 nm. The Plackett-Burman Design (PBD) was used to study three elements that influence the F0/F ratio, with the best ratio obtained with a pH of 10, for 10 min, and an aqueous reaction medium. Cu (II) was detected over a dynamic range of 4.9-197.5 μM and limit of detection (LOD) of 0.01 μM. Validation testing proved the accuracy and precision for evaluating tap and mountain waters with great selectivity and no interference from coexisting metal ions.
Keywords: Plackett–Burman Design; carbon dots; copper (II) detection; fluorescence sensor; hydrothermal process; mandarin peels biochar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Shabbir H., Csapó E., Wojnicki M. Carbon Quantum Dots: The Role of Surface Functional Groups and Proposed Mechanisms for Metal Ion Sensing. Inorganics. 2023;11:262. doi: 10.3390/inorganics11060262. - DOI
-
- Sharma V., Tiwari P., Kaur N., Mobin S.M. Optical nanosensors based on fluorescent carbon dots for the detection of water contaminants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021;19:3229–3241. doi: 10.1007/s10311-021-01241-8. - DOI
-
- Stepanidenko E.A., Vedernikova A.A., Badrieva Z.F., Brui E.A., Ondar S.O., Miruschenko M.D., Volina O.V., Koroleva A.V., Zhizhin E.V., Ushakova E.V. Manganese-Doped Carbon Dots as a Promising Nanoprobe for Luminescent and Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Photonics. 2023;10:757. doi: 10.3390/photonics10070757. - DOI
-
- El-Azazy M., Osman A.I., Nasr M., Ibrahim Y., Al-Hashimi N., Al-Saad K., Al-Ghouti M.A., Shibl M.F., Ala’a H., Rooney D.W. The interface of machine learning and carbon quantum dots: From coordinated innovative synthesis to practical application in water control and electrochemistry. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024;517:215976. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.215976. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

