Effect of Three Commercially Available Extenders Containing Phospholipids of Different Sources on Skopelos Buck Liquid-Stored Sperm Quality
- PMID: 39453086
- PMCID: PMC11512305
- DOI: 10.3390/vetsci11100494
Effect of Three Commercially Available Extenders Containing Phospholipids of Different Sources on Skopelos Buck Liquid-Stored Sperm Quality
Abstract
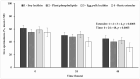
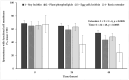
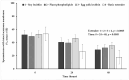
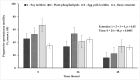
The effect of four extenders on buck semen quality parameters was examined during a 48 h liquid storage. Semen was collected from six Skopelos bucks and diluted in the following extenders, containing: soy lecithin (SL, OviXcell®), plant phospholipids (PP, AndroMed®), egg yolk lecithin (EY, Steridyl®), or no phospholipids (basic extender). Samples were stored at 5 °C for 48 h and assessed at 0, 24 and 48 h for viability (eosin-nigrosin), acrosome integrity (SpermBlue®), membrane functional integrity (HOST), mitochondrial function (Rhodamine 123/SYBR-14/PI) and motility parameters (CASA). No significant reduction in total or progressive spermatozoa motility and mitochondrial function was observed at 24 h, whereas they all dropped significantly at 48 h, in all extenders. Spermatozoa viability, cell membrane functionality and acrosome integrity dropped progressively (0 h > 24 h > 48 h) in all groups. No significant difference among extenders was observed concerning spermatozoa mitochondrial function. Overall, spermatozoa viability, cell membrane functionality and acrosome integrity were higher in the three commercial extenders, compared to the basic extender. SL and EY extenders (OviXcell® and Steridyl®, respectively) preserved viability more effectively than the PP extender (AndroMed®). Total motility was higher in the PP extender, compared to the SL extender. Spermatozoa acrosome integrity tended to be higher in the EY extender compared to all the other extenders. Further investigation of the protective potential of different types of cryoprotectants on liquid buck semen storage is important.
Keywords: buck semen; egg yolk; extender; liquid storage; plant phospholipids; soy lecithin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Van Arendonk J.A.M. The Role of Reproductive Technologies in Breeding Schemes for Livestock Populations in Developing Countries. Livest. Sci. 2011;136:29–37. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2010.09.004. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

