CYRI controls epidermal wound closure and cohesion of invasive border cell cluster in Drosophila
- PMID: 39453414
- PMCID: PMC11519390
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.202310153
CYRI controls epidermal wound closure and cohesion of invasive border cell cluster in Drosophila
Abstract
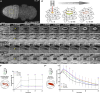
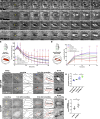
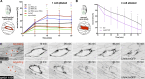
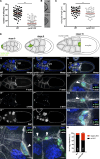
Cell motility is crucial for many biological processes including morphogenesis, wound healing, and cancer invasion. The WAVE regulatory complex (WRC) is a central Arp2/3 regulator driving cell motility downstream of activation by Rac GTPase. CYFIP-related Rac1 interactor (CYRI) proteins are thought to compete with WRC for interaction with Rac1 in a feedback loop regulating lamellipodia dynamics. However, the physiological role of CYRI proteins in vivo in healthy tissues is unclear. Here, we used Drosophila as a model system to study CYRI function at the cellular and organismal levels. We found that CYRI is not only a potent WRC regulator in single macrophages that controls lamellipodial spreading but also identified CYRI as a molecular brake on the Rac-WRC-Arp2/3 pathway to slow down epidermal wound healing. In addition, we found that CYRI limits invasive border cell migration by controlling cluster cohesion and migration. Thus, our data highlight CYRI as an important regulator of cellular and epithelial tissue dynamics conserved across species.
© 2024 Rötte et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fam49/CYRI interacts with Rac1 and locally suppresses protrusions.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Oct;20(10):1159-1171. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0198-9. Epub 2018 Sep 24. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30250061 Free PMC article.
-
CYRI/ Fam49 Proteins Represent a New Class of Rac1 Interactors.Commun Integr Biol. 2019 Jul 23;12(1):112-118. doi: 10.1080/19420889.2019.1643665. eCollection 2019. Commun Integr Biol. 2019. PMID: 31413787 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of CYRI-B (FAM49B), a key regulator of cellular actin assembly.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2020 Oct 1;76(Pt 10):1015-1024. doi: 10.1107/S2059798320010906. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2020. PMID: 33021503 Free PMC article.
-
Actin dynamics in cell migration.Essays Biochem. 2019 Oct 31;63(5):483-495. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190015. Essays Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31551324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Requirements for and consequences of Rac-dependent protrusion.Eur J Cell Biol. 2014 May-Jun;93(5-6):184-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2014.01.008. Epub 2014 Feb 11. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24629839 Review.
Cited by
-
A large reverse-genetic screen identifies numerous regulators of testis nascent myotube collective cell migration and collective organ sculpting.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Feb 1;36(2):ar21. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-10-0456. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 39745864 Free PMC article.
-
The tumor suppressor RASSF8: A WAVE interaction partner controlling migration and cohesion of invasive border cells in Drosophila.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 10;122(23):e2426702122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2426702122. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40465620 Free PMC article.
-
Plexin/Semaphorin antagonism orchestrates collective cell migration and organ sculpting by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal balance.Sci Adv. 2025 Jun 20;11(25):eadu3741. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu3741. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40532000 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting novel regulated cell death: disulfidptosis in cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Biomark Res. 2025 Feb 26;13(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s40364-025-00748-4. Biomark Res. 2025. PMID: 40012016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Böttcher, R., Hollmann M., Merk K., Nitschko V., Obermaier C., Philippou-Massier J., Wieland I., Gaul U., and Förstemann K.. 2014. Efficient chromosomal gene modification with CRISPR/cas9 and PCR-based homologous recombination donors in cultured Drosophila cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:e89. 10.1093/nar/gku289 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

