A Non-targeted Proteomics Newborn Screening Platform for Inborn Errors of Immunity
- PMID: 39453496
- PMCID: PMC11511704
- DOI: 10.1007/s10875-024-01821-7
A Non-targeted Proteomics Newborn Screening Platform for Inborn Errors of Immunity
Abstract
Purpose: Newborn screening using dried blood spot (DBS) samples for the targeted measurement of metabolites and nucleic acids has made a substantial contribution to public healthcare by facilitating the detection of neonates with genetic disorders. Here, we investigated the applicability of non-targeted quantitative proteomics analysis to newborn screening for inborn errors of immunity (IEIs).
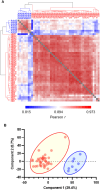
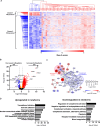
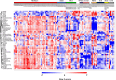
Methods: DBS samples from 40 healthy newborns and eight healthy adults were subjected to non-targeted proteomics analysis using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry after removal of the hydrophilic fraction. Subsequently, DBS samples from 43 IEI patients were analyzed to determine whether patients can be identified by reduced expression of disease-associated proteins.
Results: DBS protein profiling allowed monitoring of levels of proteins encoded by 2912 genes, including 1110 listed in the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man database, in healthy newborn samples, and was useful in identifying patients with IEIs by detecting reduced levels of disease causative proteins and their interacting proteins, as well as cell-phenotypical alterations.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that non-targeted quantitative protein profiling of DBS samples can be used to identify patients with IEIs and develop a novel newborn screening platform for genetic disorders.
Keywords: Dried blood spot; Newborn screening; Non-targeted proteomics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Guthrie R, Susi A. A Simple Phenylalanine Method for Detecting Phenylketonuria in Large Populations of Newborn Infants. Pediatrics. 1963;32:338–43. - PubMed
-
- Wilcken B, Wiley V, Hammond J, Carpenter K. Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N Engl J Med. 2003;348(23):2304–12. - PubMed
-
- Spiekerkoetter U, Bick D, Scott R, Hopkins H, Krones T, Gross ES, et al. Genomic newborn screening: Are we entering a new era of screening? J Inherit Metab Dis. 2023;46(5):778–95. - PubMed
-
- Ulph F, Bennett R. Psychological and Ethical Challenges of Introducing Whole Genome Sequencing into Routine Newborn Screening: Lessons Learned from Existing Newborn Screening. New Bioeth. 2023;29(1):52–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

