Determination of the mean duration of recent infection and false recency rate for the HIV triplex multiplex bead assay
- PMID: 39453903
- PMCID: PMC11508083
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311829
Determination of the mean duration of recent infection and false recency rate for the HIV triplex multiplex bead assay
Abstract
Background: We developed the HIV Triplex multiplex bead assay to identify and serotype HIV infection with high sensitivity and specificity; and distinguish recent from long-term HIV-1 infections. It can facilitate accurate incidence estimation, while reducing the number of tests and blood collected, which is highly desirable for use in future studies and surveys. Using previously collected, treatment-naive longitudinal seroconversion HIV-1 positive panels and specimens from individuals infected for >12 months, we determined the assay's mean duration of recent infection (MDRI) and false-recency rate (FRR) respectively, at various mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) cutoffs.
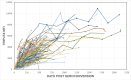
Methods: We tested seroconversion specimens (N = 814) from 142 individuals infected with HIV-1 subtypes B, C, or AE, and 1341 cross-sectional specimens from individuals infected >12 months. The MFI cutoffs of 1000 to 2000 were evaluated for recency classification, including an MFI of 1250 corresponding to the limiting antigen avidity enzyme immunoassay (LAg-EIA) cutoff of 1.5 normalized optical density for MDRI and FRR. We used four statistical methods: Methods 1 and 2 used the empirically balanced observation time approach. Method 2 MFI values were raised to power = 1.33, based on a repeated measures model to linearize the relationship between MFI and time points, whereas Method 1 was not linearized. Methods 3 and 4 employed quadratic and linear interpolations for each seroconversion panel. FRR was calculated by dividing the number of specimens misclassified as recent by the total number of specimens tested.
Results: MDRI values ranged from 135-146 days at MFI = 1000 to 229-279 days at MFI = 2000 by the 4 methods. FRR varied from 0.15%-1.27% with increasing MFI cutoff. At MFI = 1250, the average MDRI of 4 methods was 169 days and ranged from 159-183 with overlapping 95% CIs and FRR = 0.52%.
Conclusion: The HIV Triplex assay demonstrates a longer dynamic range compared to current HIV recency assays with a low FRR for cutoffs examined. With a longer dynamic range and low FRR, the MDRI for recent infection can be extended as appropriate to detect more recent infections, increasing the value of incidence assays benefiting public health surveillance and future surveys.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- PEPFAR. PEPFAR Latest Global Results: PEPFAR; 2022 Available from: https://www.pepfar.gov/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/PEPFAR-Latest-Global-R....
-
- UNAIDS. UNAIDS Fact Sheet 2022: UNAIDS; 2022 Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- UNAIDS. Global AIDS Strategy 2021–2026 ‐ End Inequalities. End AIDS.: UNAIDS; 2021 Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/Global-AIDS-Strategy-2021-2026.
-
- UNAIDS. In Danger: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022: UNAIDS; 2022 Available from: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2022/in-danger-global-aids....
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

