Application of FISH based G2-PCC assay for the cytogenetic assessment of high radiation dose exposures: Potential implications for rapid triage biodosimetry
- PMID: 39453904
- PMCID: PMC11508073
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312564
Application of FISH based G2-PCC assay for the cytogenetic assessment of high radiation dose exposures: Potential implications for rapid triage biodosimetry
Abstract
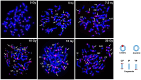
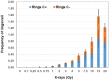
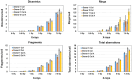
The main goal of this study is to test the utility of calyculin A induced G2-PCC assay as a biodosimetry triage tool for assessing a wide range of low and acute high radiation dose exposures of photons. Towards this initiative, chromosome aberrations induced by low and high doses of x-rays were evaluated and characterized in G2-prematurely condensed chromosomes (G2-PCCs) by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using human centromere and telomere specific PNA (peptide nucleic acid) probes. A dose dependent increase in the frequency of dicentric chromosomes was observed in the G2-PCCs up to 20 Gy of x-rays. The combined yields of dicentrics and rings in the G2-PCCs showed a clear dose dependency up to 20 Gy from 0.02/cell for 0.1 Gy to 14.98/cell for 20 Gy. Centric rings were observed more frequently than acentric ring chromosomes in the G2-PCCs at all the radiation doses from 1 Gy to 20 Gy. A head-to-head comparison was also performed by FISH on the yields of chromosome aberrations induced by different doses of x-rays (0 Gy -7.5 Gy) in colcemid arrested metaphase chromosomes and calyculin A induced G2-PCCs. In general, the frequencies of dicentrics, rings and acentric fragments were slightly higher in G2-PCCs than in colcemid arrested metaphase chromosomes at all the radiation doses, but the differences were not statistically significant. To reduce the turnaround time for absorbed radiation dose estimation, attempt was made to obtain G2-PCCs by reducing the culture time to 36 hrs. The absorbed doses estimated in x-rays irradiated (0,1,2 and 4 Gy) G2-PCCs after 36 hrs of culture were grossly like that of G2-PCCs and colcemid arrested metaphase chromosomes prepared after 48 hrs of culture. Our study indicates that the shortened version of calyculin A induced G2-PCC assay coupled with the FISH staining technique can serve as an effective triage biodosimetry tool for large-scale radiological/nuclear incidents.
Copyright: © 2024 Smith et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Triage biodosimetry using centromeric/telomeric PNA probes and Giemsa staining to score dicentrics or excess fragments in non-stimulated lymphocyte prematurely condensed chromosomes.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015 Nov;793:107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2015.06.013. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2015. PMID: 26520380
-
Suitability of scoring PCC rings and fragments for dose assessment after high-dose exposures to ionizing radiation.Mutat Res. 2013 Sep 18;757(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.03.013. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23872317
-
Simple biodosimetry method for use in cases of high-dose radiation exposure that scores the chromosome number of Giemsa-stained drug-induced prematurely condensed chromosomes (PCC).Int J Radiat Biol. 2005 Jan;81(1):33-40. doi: 10.1080/09553000500092319. Int J Radiat Biol. 2005. PMID: 15962761
-
Health impacts of large releases of radionuclides. Cytogenetic effects as quantitative indicators of radiation exposure.Ciba Found Symp. 1997;203:188-99; discussion 199-204, 232-4. Ciba Found Symp. 1997. PMID: 9339319 Review.
-
Current status of biodosimetry based on standard cytogenetic methods.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2010 Nov;49(4):567-81. doi: 10.1007/s00411-010-0311-3. Epub 2010 Jul 9. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20617329 Review.
References
-
- Gotoh E. G2 Premature Chromosome Condensation/Chromosome Aberration Assay: Drug-Induced Premature Chromosome Condensation (PCC) Protocols and Cytogenetic Approaches in Mitotic Chromosome and Interphase Chromatin for Radiation Biology. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1984:47–60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9432-8_6 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pantelias GE. Radiation-induced cytogenetic damage in relation to changes in interphase chromosome conformation. Radiat Res. 1986;105(3):341–50. . - PubMed
-
- Coco-Martin JM, Begg AC. Detection of radiation-induced chromosome aberrations using fluorescence in situ hybridization in drug-induced premature chromosome condensations of tumour cell lines with different radiosensitivities. Int J Radiat Biol. 1997;71(3):265–73. doi: 10.1080/095530097144148 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

