High keratinase and other types of hydrolase activity of the new strain of Bacillus paralicheniformis
- PMID: 39453952
- PMCID: PMC11508186
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0312679
High keratinase and other types of hydrolase activity of the new strain of Bacillus paralicheniformis
Abstract
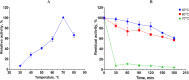
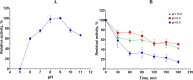
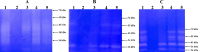
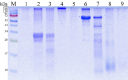
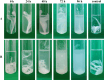
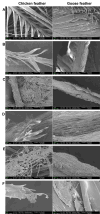
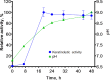
Keratinases, a subclass of proteases, are used to degrade keratin thereby forming peptones and free amino acids. Bacillus paralicheniformis strain T7 was isolated from soil and exhibited high keratinase, protease, collagenase, amylase, xylanase, lipase, and phosphatase activities. Keratinases of the strain showed maximum activity at 70°C and pH 9.0 as well as high thermal stability. A mass-spectrometric analysis identified seven peptidases with molecular masses of 26.8-154.8 kDa in the secretory proteome. These peptidases are members of S8 and S41 serine peptidase families and of M14, M42, and M55 metallopeptidase families. Additionally, α-amylase (55.2 kDa), alkaline phosphatase (59.8 kDa), and esterase (26.8 kDa) were detected. The strong keratinolytic properties of the strain were confirmed by degradation of chicken and goose feathers, which got completely hydrolyzed within 4 days. Submerged fermentation by strain B. paralicheniformis T7 was carried out in a pilot bioreactor, where the highest keratinase production was noted after 19 h of cultivation. After the fermentation, in the culture fluid, the keratinase activity toward keratin azure was 63.6 ± 5.8 U/mL. The protease activity against azocasein was 715.7 ± 40.2 U/mL. The possibility of obtaining enzyme preparations in liquid and powder form was demonstrated, and their comparative characteristics are given. In the concentrate, the keratinase, protease, α-amylase, phosphatase, and esterase/lipase activities were 2,656.7 ± 170.4, 29,886.7 ± 642.9, 176.1 ± 16.3, 23.9 ± 1.8, and 510.9 ± 12.2 U/mL, respectively. In the lyophilizate, these activities were 57,733.3 ± 8,911.4, 567,066.7 ± 4,822.2, 2,823.0 ± 266.8, 364.2 ± 74.8, and 17,618.0 ± 610.3 U/g, respectively. In the preparation obtained by air flow drying at 55°C, these activities were 53,466.7 ± 757.2, 585,333.3 ± 4,277.1, 2,395.8 ± 893.7, 416.7 ± 52.4, and 15,328.1 ± 528.6 U/g, respectively. The results show high potential of B. paralicheniformis strain T7 as a producer of keratinases and other enzymes for applications in agricultural raw materials and technologies for processing of keratin-containing animal waste.
Copyright: © 2024 Aktayeva, Khassenov. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Wang B, Yang W, McKittrick J, Meyers MA. Keratin: Structure, mechanical properties, occurrence in biological organisms, and efforts at bioinspiration. Progress in Materials Science. 2016;76:229–318. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2015.06.001 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

