Efficient electroporation in primary cells with PEDOT:PSS electrodes
- PMID: 39454003
- PMCID: PMC11506140
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ado5042
Efficient electroporation in primary cells with PEDOT:PSS electrodes
Abstract
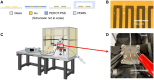
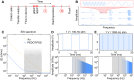
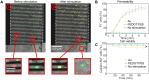
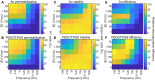
Precise and efficient delivery of macromolecules into cells enhances basic biology research and therapeutic applications in cell therapies, drug delivery, and personalized medicine. While pulsed electric field electroporation effectively permeabilizes cell membranes to deliver payloads without the need for toxic chemical or viral transduction agents, conventional bulk electroporation devices face major challenges with cell viability and heterogeneity due to variations in fields generated across cells and electrochemistry at the electrode-electrolyte interface. Here, we introduce the use of microfabricated electrodes based on the conducting polymer poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with polystyrene sulfonate (PEDOT:PSS), which substantially increases cell viability and transfection efficiency. As a proof of concept, we demonstrate the enhanced delivery of Cas9 protein, guide RNA, and plasmid DNA into cell lines and primary cells. This use of PEDOT:PSS enables rapid modification of difficult-to-transfect cell types to accelerate their study and use as therapeutic platforms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Conductive Polymer PEDOT:PSS-Based Platform for Embryonic Stem-Cell Differentiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 20;23(3):1107. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031107. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163031 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Conductive PEDOT:PSS Films with 1,3-Dimethyl-2-Imidazolidinone as Transparent Electrodes for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016 Sep;37(17):1427-33. doi: 10.1002/marc.201600144. Epub 2016 Jul 5. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2016. PMID: 27377555
-
Autoclave Sterilization of PEDOT:PSS Electrophysiology Devices.Adv Healthc Mater. 2016 Dec;5(24):3094-3098. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600870. Epub 2016 Nov 25. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016. PMID: 27885829
-
Applications of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) doped with poly(styrene sulfonic acid) transistors in chemical and biological sensors.Chem Rec. 2008;8(1):13-22. doi: 10.1002/tcr.20133. Chem Rec. 2008. PMID: 18302284 Review.
-
New directions in medical biosensors employing poly(3,4-ethylenedioxy thiophene) derivative-based electrodes.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009 Oct;395(3):637-45. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2981-8. Epub 2009 Jul 31. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009. PMID: 19644677 Review.
Cited by
-
Conductive MeCbl/PEDOT:PSS/HA hydrogels with electrical stimulation for enhanced peripheral nerve regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Apr 10;32:101755. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101755. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40290882 Free PMC article.
-
Poly(3-hexylthiophene) as a versatile semiconducting polymer for cutting-edge bioelectronics.Mater Horiz. 2025 Jul 28;12(15):5570-5593. doi: 10.1039/d5mh00096c. Mater Horiz. 2025. PMID: 40331312 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hapala I., Breaking the barrier: Methods for reversible permeabilization of cellular membranes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 17, 105–122 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Diacumakos E. G., Methods for micromanipulation of human somatic cells in culture. Methods Cell Biol. 7, 287–311 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J., A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology 52, 456–467 (1973). - PubMed
-
- Hamer D. H., Leder P., Expression of the chromosomal mouse Beta maj-globin gene cloned in SV40. Nature 281, 35–40 (1979). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

