Temporal regulation of gene expression through integration of p53 dynamics and modifications
- PMID: 39454005
- PMCID: PMC11506164
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adp2229
Temporal regulation of gene expression through integration of p53 dynamics and modifications
Abstract
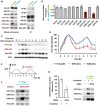
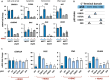
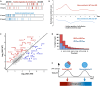
The master regulator of the DNA damage response, the transcription factor p53, orchestrates multiple downstream responses and coordinates repair processes. In response to double-strand DNA breaks, p53 exhibits pulses of expression, but how it achieves temporal coordination of downstream responses remains unclear. Here, we show that p53's posttranslational modification state is altered between its first and second pulses of expression. We show that acetylations at two sites, K373 and K382, were reduced in the second pulse, and these acetylations differentially affected p53 target genes, resulting in changes in gene expression programs over time. This interplay between dynamics and modification may offer a strategy for cellular hubs like p53 to temporally organize multiple processes in individual cells.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

