Orientation-dependent CD45 inhibition with viral and engineered ligands
- PMID: 39454026
- PMCID: PMC11537708
- DOI: 10.1126/sciimmunol.adp0707
Orientation-dependent CD45 inhibition with viral and engineered ligands
Abstract
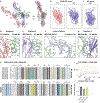
CD45 is a cell surface phosphatase that shapes the T cell receptor signaling threshold but does not have a known ligand. A family of adenovirus proteins, including E3/49K, exploits CD45 to evade immunity by binding to the extracellular domain of CD45, resulting in the suppression of T cell signaling. We determined the cryo-EM structure of this complex and found that the E3/49K protein is composed of three immunoglobulin domains assembled as "beads on a string" that compel CD45 into a closely abutted dimer by cross-linking the CD45 D3 domain, leading to steric inhibition of its intracellular phosphatase activity. Inspired by the E3/49K mechanism, we engineered CD45 surrogate ligands that can fine-tune T cell activation by dimerizing CD45 into different orientations and proximities. The adenovirus E3/49K protein has taught us that, despite a lack of a known ligand, CD45 activity can be modulated by extracellular dimerizing ligands that perturb its phosphatase activity and alter T cell responses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
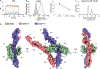

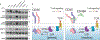
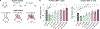
References
-
- Ostergaard HL, Trowbridge IS, Negative Regulation of CD45 Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Activity by Ionomycin in T Cells. Science 253, 1423–1425 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Hermiston ML, Xu Z, Weiss A, CD45: A Critical Regulator of Signaling Thresholds in Immune Cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 21, 107–137 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Koretzky GA, Picus J, Thomas ML, Arthur. Weiss, Tyrosine phosphatase CD45 is essential for coupling T-cell antigen receptor to the phosphatidyl inositol pathway. Nature 346, 66–68 (1990). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

