Method of moments framework for differential expression analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data
- PMID: 39454576
- PMCID: PMC11556465
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.044
Method of moments framework for differential expression analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data
Abstract
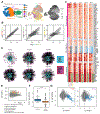
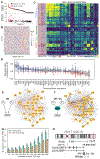
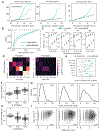
Differential expression analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data is central for characterizing how experimental factors affect the distribution of gene expression. However, distinguishing between biological and technical sources of cell-cell variability and assessing the statistical significance of quantitative comparisons between cell groups remain challenging. We introduce Memento, a tool for robust and efficient differential analysis of mean expression, variability, and gene correlation from scRNA-seq data, scalable to millions of cells and thousands of samples. We applied Memento to 70,000 tracheal epithelial cells to identify interferon-responsive genes, 160,000 CRISPR-Cas9 perturbed T cells to reconstruct gene-regulatory networks, 1.2 million peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to map cell-type-specific quantitative trait loci (QTLs), and the 50-million-cell CELLxGENE Discover corpus to compare arbitrary cell groups. In all cases, Memento identified more significant and reproducible differences in mean expression compared with existing methods. It also identified differences in variability and gene correlation that suggest distinct transcriptional regulation mechanisms imparted by perturbations.
Keywords: Bootstrap method; CD4 T cells; CELLxGENE Discover; Differential expression; Gene expression variance; Gene-regulatory networks; Memento; Single-cell transcriptomics; Spatial genomics; scRNA-seq analysis.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.J.Y. is founder for and holds equity in DropPrint Genomics (now ImmunAI) and Survey Genomics; a Scientific Advisory Board member for and holds equity in Related Sciences and ImmunAI; and a consultant for and holds equity in Maze Therapeutics. C.J.Y. has received research support from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Chan Zuckerberg Biohub, Arc Institute, Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, Genentech, BioLegend, ScaleBio, and Illumina. A.M. is a co-founder of Site Tx, Arsenal Biosciences, Spotlight Therapeutics, and Survey Genomics; serves on the boards of directors of Site Tx, Spotlight Therapeutics, and Survey Genomics; and is a member of the scientific advisory boards of Site Tx, Arsenal Biosciences, Cellanome, Spotlight Therapeutics, Survey Genomics, NewLimit, Amgen, and Tenaya. A.M. owns stock in Arsenal Biosciences, Site Tx, Cellanome, Spotlight Therapeutics, NewLimit, Survey Genomics, Tenaya, and Lightcast and has received fees from Site Tx, Arsenal Biosciences, Cellanome, Spotlight Therapeutics, NewLimit, Gilead, Pfizer, 23andMe, PACT Pharma, Juno Therapeutics, Tenaya, Lightcast, Trizell, Vertex, Merck, Amgen, Genentech, GLG, ClearView Healthcare, AlphaSights, Rupert Case Management, Bernstein, and ALDA. A.M. is an investor in and informal advisor to Offline Ventures and a client of EPIQ. The Marson laboratory has received research support from the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy, the Emerson Collective, Arc Institute, Juno Therapeutics, Epinomics, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, and Anthem and reagents from Genscript and Illumina.
Figures



References
-
- Newman JRS, Ghaemmaghami S, Ihmels J, Breslow DK, Noble M, DeRisi JL, and Weissman JS (2006). “Single-cell proteomic analysis of S. cerevisiae reveals the architecture of biological noise”. en. Nature 441.7095, pp. 840–846. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

