Lateral Flow-Based Skin Patch for Rapid Detection of Protein Biomarkers in Human Dermal Interstitial Fluid
- PMID: 39455057
- PMCID: PMC11590092
- DOI: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00956
Lateral Flow-Based Skin Patch for Rapid Detection of Protein Biomarkers in Human Dermal Interstitial Fluid
Abstract
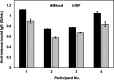
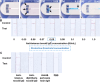
Rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) offer valuable diagnostic information in a quick, easy-to-use and low-cost format. While RDTs are one of the most commonly used tools for in vitro diagnostic testing, they require the collection of a blood sample, which is painful, poses risks of infection and can lead to complications. We introduce a blood-free point-of-care diagnostic test for the rapid detection of protein biomarkers in dermal interstitial fluid (ISF). This device consists of a lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (LFIA) integrated within a microfluidic skin patch. ISF is collected from the skin using a microneedle array and vacuum-assisted extraction system integrated in the patch, and transported through the lateral flow strip via surface tension. Using this skin patch platform, we demonstrate in situ detection of anti-tetanus toxoid IgG and SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, which could be accurately detected in human ISF in <20 min. We envision that this device can be readily modified to detect other protein biomarkers in dermal ISF, making it a promising tool for rapid diagnostic testing.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; diagnostic; interstitial fluid; lateral flow immunoassay; microfluidic; skin; tetanus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): E.C.W. and P.B.L. are co-inventors of a provisional patent application filed by Rice University on the subject of this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

