Thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms: a viewpoint on its impact on myelofibrosis, mortality, and solid tumors
- PMID: 39455571
- PMCID: PMC11512069
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-024-01169-6
Thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms: a viewpoint on its impact on myelofibrosis, mortality, and solid tumors
Abstract
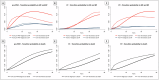
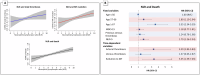
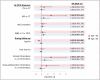
This viewpoint summarizes findings from analyses of large personal patient databases of myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) to assess the impact of thrombosis on mortality, disease progression, and second cancers (SC). Despite advances, the current incidence of arterial and venous thrombosis remains a challenge. These events appear to signal a more aggressive disease course, as evidenced by their association with myelofibrosis progression and mortality using multistate models and time-dependent multivariable analysis. Inflammatory biomarkers, such as the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), are associated with the aggressiveness of polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocythemia (ET), linking thrombosis to SC risk. This suggests a common inflammatory pathway likely influencing cardiovascular disease and cancer incidence. Notably, this is observed more frequently in younger patients, likely due to prolonged exposure to MPN and environmental inflammatory triggers. These data underscore the need for new studies to validate these associations, delineate the sequence of events, and identify therapeutic targets to mitigate thrombotic events and potentially improve overall patient outcomes in MPN.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Barosi G, Mesa RA, Thiele J, Cervantes F, Campbell PJ, Verstovsek S, et al. Proposed criteria for the diagnosis of post-polycythemia vera and post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis: a consensus statement from the International Working Group for Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Leukemia. 2008;22:437–8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

