Regulation of hepatic inclusions and fibrinogen biogenesis by SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD
- PMID: 39455574
- PMCID: PMC11512042
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-53639-x
Regulation of hepatic inclusions and fibrinogen biogenesis by SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD
Abstract
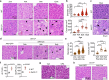
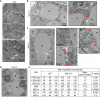
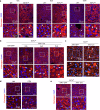
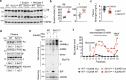
Impaired secretion of an essential blood coagulation factor fibrinogen leads to hepatic fibrinogen storage disease (HFSD), characterized by the presence of fibrinogen-positive inclusion bodies and hypofibrinogenemia. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying the biogenesis of fibrinogen in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) remain unexplored. Here we uncover a key role of SEL1L-HRD1 complex of ER-associated degradation (ERAD) in the formation of aberrant inclusion bodies, and the biogenesis of nascent fibrinogen protein complex in hepatocytes. Acute or chronic deficiency of SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD in the hepatocytes leads to the formation of hepatocellular inclusion bodies. Proteomics studies followed by biochemical assays reveal fibrinogen as a major component of the inclusion bodies. Mechanistically, we show that the degradation of misfolded endogenous fibrinogen Aα, Bβ, and γ chains by SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD is indispensable for the formation of a functional fibrinogen complex in the ER. Providing clinical relevance of these findings, SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD indeed degrades and thereby attenuates the pathogenicity of two disease-causing fibrinogen γ mutants. Together, this study demonstrates an essential role of SEL1L-HRD1 ERAD in fibrinogen biogenesis and provides insight into the pathogenesis of protein-misfolding diseases.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures


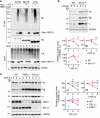
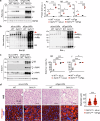

References
-
- Casini A., Neerman-Arbez M., & de Moerloose P. Heterogeneity of congenital afibrinogenemia, from epidemiology to clinical consequences and management. Blood Rev. 100793 (2020). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK090313/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- U01 CA274304/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL166382/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
- R01DK128077/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01DK132068/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R01 HL168009/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK090313/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK126908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK126908/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (National Institute of Diabetes & Digestive & Kidney Diseases)
- R21HD104904/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD)
- R01HL163516/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

