Prognostic potential of standard laboratory parameters in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer receiving first-line immunotherapy
- PMID: 39455722
- PMCID: PMC11511985
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76928-3
Prognostic potential of standard laboratory parameters in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer receiving first-line immunotherapy
Abstract
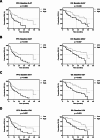
Through their involvement in cancer metabolism, alanine aminotransferase (ALAT), aspartate aminotransferase (ASAT), γ-glutamyltransferase (GGT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) reflect the tumor burden and thus could have a prognostic potential for patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPI). Therefore, this study investigated the prognostic potential of these parameters in a real-world cohort of patients with metastatic renal cell cancer (mRCC) under first-line CPI-based therapy. The retrospective study cohort included 82 mRCC patients treated with CPI-based first-line therapy between 2019 and 2023. Progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS) and response rates were evaluated according to baseline levels and early dynamic changes of ALAT, ASAT, GGT and LDH. Multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models were generated to identify independent prognosticators for PFS and OS. High baseline levels and non-normalized kinetics of ALAT, ASAT, GGT and LDH were significantly associated with shorter PFS and OS (p < 0.05), which was also reflected by lower response rates. Combining the four parameters at baseline into a 4-Risk-Score resulted in an enhanced prognostic power, as indicated by a higher C-index of 0.693 for OS compared to the individual parameters (≤ 0.663). Patients with all four risk factors present showed the worst PFS and OS. Overall, baseline levels and early kinetics of the four parameters as well as the 4-Risk-Score were identified as independent prognosticators for PFS and OS by multivariate analysis. As standard laboratory parameters, ALAT, ASAT, GGT and LDH are cost-effective and could be easily used either alone or in combination for therapy monitoring of CPI-treated mRCC patients.
Keywords: Early kinetics; Immune checkpoint inhibitors; Lactate dehydrogenase; Metastatic renal cell cancer; Prognostic biomarkers; γ-Glutamyltransferase.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Early kinetics of C-reactive protein as prognosticator for survival in a real-world cohort of patients with metastatic renal cell cancer under first-line therapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 May;26(5):1117-1128. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03317-z. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37695463 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of the pretreatment aspartate transaminase/alanine transaminase ratio in patients treated with first-line systemic tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.Int J Urol. 2018 Jun;25(6):596-603. doi: 10.1111/iju.13574. Epub 2018 May 13. Int J Urol. 2018. PMID: 29756394
-
Lactate Dehydrogenase-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Represents a Powerful Prognostic Tool of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Apr;26(2):1319-1324. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00707-z. Epub 2019 Aug 6. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31388933
-
Prognostic role of pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2020 Jul;79:66-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.05.019. Epub 2020 May 14. Int J Surg. 2020. PMID: 32417461
-
Immunotherapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A brief history, current trends, and future directions.Urol Oncol. 2021 Oct;39(10):664-677. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2021.06.013. Epub 2021 Jul 24. Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34312081 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic effect of pretreatment serum gamma-glutamyl transferase in urological malignancies: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 25;15:1597155. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1597155. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40636684 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray, F. et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin.74, 229–263. 10.3322/caac.21834 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Bedke, J. et al. Updated European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib joins Immune Checkpoint Inhibition Combination therapies for treatment-naive metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol.79, 339–342. 10.1016/j.eururo.2020.12.005 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Xu, W., Atkins, M. B. & McDermott, D. F. Checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy in kidney cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol.17, 137–150. 10.1038/s41585-020-0282-3 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Ljungberg, B. et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: the 2022 Update. Eur. Urol.82, 399–410. 10.1016/j.eururo.2022.03.006 (2022). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

