Comprehensive genome analysis and variant detection at scale using DRAGEN
- PMID: 39455800
- PMCID: PMC12022141
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-024-02382-1
Comprehensive genome analysis and variant detection at scale using DRAGEN
Abstract
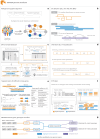
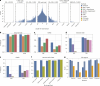
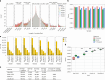
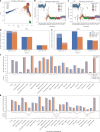
Research and medical genomics require comprehensive, scalable methods for the discovery of novel disease targets, evolutionary drivers and genetic markers with clinical significance. This necessitates a framework to identify all types of variants independent of their size or location. Here we present DRAGEN, which uses multigenome mapping with pangenome references, hardware acceleration and machine learning-based variant detection to provide insights into individual genomes, with ~30 min of computation time from raw reads to variant detection. DRAGEN outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in speed and accuracy across all variant types (single-nucleotide variations, insertions or deletions, short tandem repeats, structural variations and copy number variations) and incorporates specialized methods for analysis of medically relevant genes. We demonstrate the performance of DRAGEN across 3,202 whole-genome sequencing datasets by generating fully genotyped multisample variant call format files and demonstrate its scalability, accuracy and innovation to further advance the integration of comprehensive genomics. Overall, DRAGEN marks a major milestone in sequencing data analysis and will provide insights across various diseases, including Mendelian and rare diseases, with a highly comprehensive and scalable platform.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: F.J.S. receives research support from Genentech, Illumina, PacBio and ONT. S.C., M.R., S.T., Z.H., M.R., A.V., G.P., C.R., A.F., V.O., S.M., J.H. and R.M. are employees of Illumina. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Tarailo-Graovac, M., Wasserman, W. W. & Van Karnebeek, C. D. M. Impact of next-generation sequencing on diagnosis and management of neurometabolic disorders: current advances and future perspectives. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn.17, 307–309 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

