A conserved Plasmodium nuclear protein is critical for late liver stage development
- PMID: 39455824
- PMCID: PMC11511937
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-024-07063-y
A conserved Plasmodium nuclear protein is critical for late liver stage development
Abstract
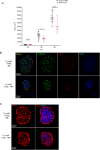
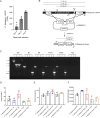
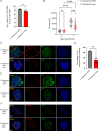
Malaria, caused by Plasmodium parasites, imposes a significant health burden and live-attenuated parasites are being pursued as vaccines. Here, we report on the creation of a genetically attenuated parasite by the deletion of Plasmodium LINUP, encoding a liver stage nuclear protein. In the rodent parasite Plasmodium yoelii, LINUP expression was restricted to liver stage nuclei after the onset of liver stage schizogony. Compared to wildtype P. yoelii, P. yoelii LINUP gene deletion parasites (linup-) exhibited no phenotype in blood stages and mosquito stages but suffered developmental arrest late in liver stage schizogony with a pronounced defect in exo-erythrocytic merozoite formation. This defect caused severe attenuation of the liver stage-to-blood stage transition and immunization of mice with linup - parasites conferred robust protection against infectious sporozoite challenge. LINUP gene deletion in the human parasite Plasmodium falciparum also caused a severe defect in late liver stage differentiation. Importantly, P. falciparum linup - liver stages completely failed to transition from the liver stage to a viable blood stage infection in a humanized mouse model. These results suggest that P. falciparum LINUP is an ideal target for late liver stage attenuation that can be incorporated into a late liver stage-arresting replication competent whole parasite vaccine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Stefan Kappe, Ashley Vaughan, and Debashree Goswami are members of the Seattle Children’s Hospital workforce, and are inventors of patents licensed to Sanaria and have revenue distribution rights arising from patents rights licensed to Sanaria. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization. World Malaria Report 2022. World Health (WHO/HTM/GM, 2022).
-
- World Health Organization, W. WHO recommends groundbreaking malaria vaccine for children at risk. https://www.who.int/news/item/06-10-2021-who-recommends-groundbreaking-m... (2021).
-
- Datoo, M. S. et al. Safety and efficacy of malaria vaccine candidate R21/Matrix-M in African children: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet403, 533–544 (2024). - PubMed
-
- Seder, R. A. et al. Protection against malaria by intravenous immunization with a nonreplicating sporozoite vaccine. Science341, 1359–1365 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

