A comparison between in vitro and randomized in situ models for remineralization of artificial enamel lesions
- PMID: 39455837
- PMCID: PMC11511857
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-76387-w
A comparison between in vitro and randomized in situ models for remineralization of artificial enamel lesions
Abstract
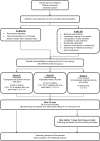
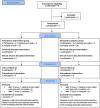
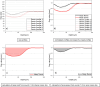
The randomized study aimed to evaluate the comparability of in situ (iS) and in vitro (iV) study protocols regarding remineralization of artificial enamel lesions. Two toothpastes (group A: 1450 ppm sodium fluoride, group B: placebo 0 ppm F-), were investigated. IV, a pH-cycling model with toothpaste slurry treatment was applied for 10d. IS, remineralization was performed in 9 participants wearing splints with embedded enamel samples for 10 and 21d, randomly allocated to groups A and B. Samples were scanned by X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT) and grayscale value line profiles corresponding to mineral density (rel.ΔZ) were analyzed. Statistical analyses were performed using MedCalc Statistical Software, v22.021. T-Test for dependent and independent data and analysis of variance (ANOVA) were used for further analyses (α = 0.05). Rel.ΔZ of fluoride treated samples (A) were iV = 40.2%, iS 10d = 11.5% and iS 21d = 46.1% (p > 0.05). Rel.ΔZ of placebo treated samples (B) were: iV = - 6.2%, iS 10d = 25.2% and iS 21d = 11.0% (p > 0.05). Remineralization potential of both toothpastes was significantly different regarding iV (p < 0.001) and iS after 21d (p = 0.034), while in case of iS 10d no significant difference was detected (p = 0.4). Despite different study protocols the μCT results after remineralization were comparable between iV and iS. The results suggest that selected studies can be carried out in faster, simplified iV studies using pH-cycling instead of iS studies.
Keywords: Demineralization; Dentifrice; Enamel; Fluoride; In-situ; In-vitro; Micro-ct; Remineralization.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Martinez-Mier, E. A. et al. European organization for caries research workshop: methodology for determination of potentially available fluoride in toothpastes. Caries Res.53, 119–136 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Pollick, H. The role of fluoride in the prevention of tooth decay. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am.65, 923–940 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

