Persistence and recurrence after removal of idiopathic epiretinal membrane
- PMID: 39455899
- PMCID: PMC11751316
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-024-03429-y
Persistence and recurrence after removal of idiopathic epiretinal membrane
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse the incidence of persistence and recurrence after the peeling of idiopathic epiretinal membrane (ERM) and to describe its clinical features.
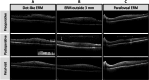
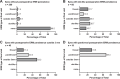
Methods: This retrospective study included 666 eyes (645 patients) that underwent macular surgery for ERM removal. Optical coherence tomographic (OCT) images taken within three months after surgery and at the following visits, clinical parameters and surgery related factors were analysed to investigate the incidence and associated factors of ERM persistence and recurrence. Postoperative ERM types were categorised depending on the size ( < 100 µm, ≥100 µm) and the location (foveal, parafoveal, outside the parafovea) RESULTS: The mean follow-up time was 29.4 months. ERM persistence (examination within 3 months) was found in 29.6% of all eyes. Only 1.9% of the eyes presented foveal ERM persistence. Foveal recurrence, defined as reappearance or growth of persistent ERM covering the fovea, was found in 8.2%. In 84.4% of eyes with foveal ERM recurrence, postoperative persistence of ERM of varying severity were identified. None of the pre-operative or surgery related factors were found significantly associated with ERM recurrence. Persistent ERM within the parafovea was the most significant risk factor for foveal ERM recurrence.
Conclusion: Recurrence of ERM is generally preceded by the persistence of ERM fragments found in the early postoperative period. Growth of ERM persistence from the parafoveal region was often the origin of foveal ERM recurrence. Insufficient peeling seems to be the most significant predisposing factor for foveal ERM recurrence.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics statement: The study was approved by the institutional review board of the medical faculty of Tübingen University (Project No. 175/2020BO2) and was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures
References
-
- Mitchell P, Smith W, Chey T, Wang JJ, Chang A. Prevalence and associations of epiretinal membranes: the blue mountains eye study, Australia. Ophthalmology. 1997;104:1033–40. - PubMed
-
- Machemer R. [The surgical removal of epiretinal macular membranes (macular puckers) (author’s transl)]. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 1978;173:36–42. - PubMed
-
- Bouwens MD, de Jong F, Mulder P, van Meurs JC. Results of macular pucker surgery: 1- and 5-year follow-up. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008;246:1693–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

