Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 39456002
- PMCID: PMC11515276
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-024-01497-4
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to provide cardiovascular benefits in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, their cardiovascular protective efficacy in high-risk T2DM patients, particularly those with a history of cardiovascular events or severe chronic kidney disease, remains uncertain.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and The Cochrane Library to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that evaluated the effects of GLP-1 RAs on cardiovascular outcomes in high-risk patients with T2DM. A random-effects model was used to calculate pooled hazard ratios (HRs) for cardiovascular outcomes. Subgroup analyses and GRADE assessment were also performed.
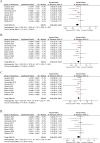
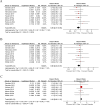
Results: Nine RCTs involving 63,613 patients were included. GLP-1 RAs significantly reduced the risk of the primary composite outcome (HR: 0.86, 95% CI: 0.80-0.92), cardiovascular death (HR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.78-0.93), all-cause death (HR: 0.87, 95% CI: 0.82-0.93), myocardial infarction (HR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.82-0.98), stroke (HR: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.77-0.95), and heart failure (HF) hospitalization (HR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.83-0.97). No significant difference in unstable angina (UA) hospitalization was observed (HR: 1.04, 95% CI: 0.95-1.15). Subgroup analyses indicated greater benefits with combination therapy, particularly in patients with chronic kidney disease. The quality of evidence was rated as "High" for six outcomes and "Moderate" for UA hospitalization.
Conclusions: GLP-1 RAs significantly reduce cardiovascular risk in high-risk T2DM patients, especially with combination therapy and in those with chronic kidney disease. However, further research is needed to confirm their long-term effects.
Keywords: Cardiovascular outcomes; Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; High-risk type 2 diabetes; Meta-analysis; Randomized controlled trials.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2):88–98. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad E, Lim S, Lamptey R, Webb DR, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 2022;400(10365):1803–20. - PubMed
-
- Nauck MA, Wefers J, Meier JJ. Treatment of type 2 diabetes: challenges, hopes, and anticipated successes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021;9(8):525–44. - PubMed
-
- Joseph JJ, Deedwania P, Acharya T, Aguilar D, Bhatt DL, Chyun DA, et al. Comprehensive Management of Cardiovascular Risk factors for adults with type 2 diabetes: a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2022;145(9):e722–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

