A review of current developments in RNA modifications in lung cancer
- PMID: 39456034
- PMCID: PMC11515118
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-024-03528-6
A review of current developments in RNA modifications in lung cancer
Abstract
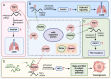
Lung cancer has the highest incidence and mortality rates worldwide and is the primary cause of cancer-related death. Despite the rapid development of diagnostic methods and targeted drugs in recent years, many lung cancer patients do not benefit from effective therapies. The emergence of drug resistance has led to a reduction in the therapeutic effectiveness of targeted drugs, highlighting a crucial need to explore novel therapeutic targets. Many studies have found that epigenetic plays an important role in the occurrence of lung cancer. This review describes the biological function of epigenetic RNA modifications, such as m6A, m5C, m7G, and m1A, and recent advancements in their role in the development, progression, and prognosis of lung cancer. This review aims to provide new guidance for the treatment of lung cancer.
Keywords: Epigenetic; Lung cancer; NSCLC; RNA modification.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Siegel RL, Jemal A. Lung cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;893:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Orsolic I, Carrier A, Esteller M. Genetic and epigenetic defects of the RNA modification machinery in cancer. Trends in Genet TIG. 2023;39(1):74–88. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

