Serum Otoconin-90 and Otolin-1 Concentrations in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
- PMID: 39456211
- PMCID: PMC11506338
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14101279
Serum Otoconin-90 and Otolin-1 Concentrations in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Abstract
Objective: The aim was to evaluate the value of otolith-associated protein otoconin-90 (OC90) and otolin-1 in the pathogenesis research and clinical treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
Material and method: The study included 50 patients with BPPV admitted to neurology and otorhinolaryngology departments and 30 healthy subjects with no history of dizziness as a control group.
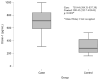
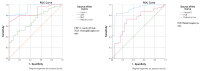
Results: BPPV and controls were similar in terms of gender and age. Otolin-1 concentration was significantly greater in the BPPV group than in the controls (710.44 [584.35-837.39] vs 280.45 [212.7-419.61]; p < 0.001). No statistical significance was found, although OC90 was higher in the BPPV group than in the controls. There was a strong positive correlation between otolin-1 and OC90, a moderate negative correlation between otolin-1 and vitamin D, and a strong negative correlation between OC90 and vitamin D in the BPPV patient group. Otolin-1 had high specificity and AUC values for BPPV (AUC: 0.933; 95% CI: 0.881-0.986, 79.2% sensitivity, 100% specificity with a cutoff greater than 525).
Conclusions: High serum concentrations of otolin-1 were associated with an increased risk of BPPV, but high concentrations of OC90 were not. Serum concentrations of otolin-1 can potentially be used as a biomarker for the acute onset of inner ear disorders due to the significant increase in patients with BPPV. Vitamin D has high specificity and sensitivity in patients with BPPV. It also provides evidence that BPPV patients with vitamin D deficiency may improve their symptoms with replacement therapy. More large-scale prospective studies are required to confirm these associations and clarify the exact mechanisms.
Keywords: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo; otolin-1; otolith-associated protein otoconin-90; vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An evaluation of serum Otolin-1 & Vitamin-D in benign paroxysmal positional vertigo.J Vestib Res. 2021;31(6):433-440. doi: 10.3233/VES-201601. J Vestib Res. 2021. PMID: 33720865
-
Increased Otolin-1 in Serum as a Potential Biomarker for Idiopathic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Episodes.Front Neurol. 2020 May 13;11:367. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00367. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32477244 Free PMC article.
-
High Serum Levels of Otolin-1 in Patients With Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Predict Recurrence.Front Neurol. 2022 Mar 14;13:841677. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.841677. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35359660 Free PMC article.
-
Association between otolin-1 and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: A meta-analysis.Front Neurol. 2022 Dec 15;13:950023. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.950023. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36601298 Free PMC article.
-
Association between serum vitamin D levels and benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Jan;277(1):169-177. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05694-0. Epub 2019 Oct 19. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31630244
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical