Interplay between the Redox System and Renal Tubular Transport
- PMID: 39456410
- PMCID: PMC11505102
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101156
Interplay between the Redox System and Renal Tubular Transport
Abstract
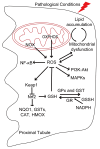
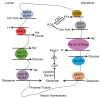
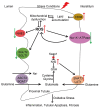
The kidney plays a critical role in maintaining the homeostasis of body fluid by filtration of metabolic wastes and reabsorption of nutrients. Due to the overload, a vast of energy is required through aerobic metabolism, which inevitably leads to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the kidney. Under unstressed conditions, ROS are counteracted by antioxidant systems and maintained at low levels, which are involved in signal transduction and physiological processes. Accumulating evidence indicates that the reduction-oxidation (redox) system interacts with renal tubular transport. Redox imbalance or dysfunction of tubular transport leads to renal disease. Here, we discuss the ROS and antioxidant systems in the kidney and outline the metabolic dysfunction that is a common feature of renal disease. Importantly, we describe the key molecules involved in renal tubular transport and their relationship to the redox system and, finally, summarize the impact of their dysregulation on the pathogenesis and progression of acute and chronic kidney disease.
Keywords: kidney; metabolism; redox system; tubular transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute stress deteriorates breast meat quality of Ross 308 broiler chickens by inducing redox imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction.J Anim Sci. 2022 Sep 1;100(9):skac221. doi: 10.1093/jas/skac221. J Anim Sci. 2022. PMID: 35713956 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species and Redox Signaling in Chronic Kidney Disease.Cells. 2020 May 28;9(6):1342. doi: 10.3390/cells9061342. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32481548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane rafts-redox signalling pathway contributes to renal fibrosis via modulation of the renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Physiol. 2018 Aug;596(16):3603-3616. doi: 10.1113/JP275952. Epub 2018 Jul 23. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29863758 Free PMC article.
-
Aging-related NOX4-Nrf2 redox imbalance increases susceptibility to cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by regulating mitophagy.Life Sci. 2024 Jan 1;336:122352. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122352. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38104863
-
Evaluating the Oxidative Stress in Renal Diseases: What Is the Role for S-Glutathionylation?Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016 Jul 20;25(3):147-64. doi: 10.1089/ars.2016.6656. Epub 2016 Apr 19. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2016. PMID: 26972776 Review.
Cited by
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors as Potential Antioxidant Therapeutic Agents in Cardiovascular and Renal Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 13;14(3):336. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030336. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227417 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

