Protective Effects of Anethole in Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Seed Ethanol Extract on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in H9C2 Heart Myoblast Cells
- PMID: 39456415
- PMCID: PMC11504384
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101161
Protective Effects of Anethole in Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Seed Ethanol Extract on Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury in H9C2 Heart Myoblast Cells
Abstract
Background: Active compounds from plants and herbs are increasingly incorporated into modern medical systems to address cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Foeniculum vulgare Mill., commonly known as fennel, is an aromatic medicinal plant and culinary herb that is popular worldwide.
Methods: Protective effects against cellular damage were assessed in the H9C2 cardiomyocyte hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R) experimental model. The identities of phytochemicals in FVSE were determined by GC-MS analysis. The phytochemical's potential for nutrients and pharmacokinetic properties was assessed by ADMET analysis.
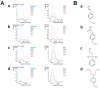
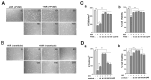
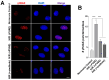
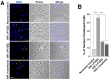
Results: GC-MS analysis of the ethanol extracts of F. vulgare identified 41 bioactive compounds, with four prominent ones: anethole, 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-2-propanone, ethoxydimethylphenylsilane, and para-anisaldehyde diethyl acetal. Among these, anethole stands out due to its potential for nutrients and pharmacokinetic properties assessed by ADMET analysis, such as bioavailability, lipophilicity, flexibility, and compliance with Lipinski's Rule of Five. In the H/R injury model of H9C2 heart myoblast cells, FVSE and anethole suppressed H/R-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, DNA double-strand break damage, nuclear condensation, and the dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm).
Conclusions: These findings highlight the therapeutic potential of FVSE and its prominent component, anethole, in the treatment of CVDs, particularly those associated with hypoxia-induced damage.
Keywords: ADMET; DNA double-strand break damage; Foeniculum vulgare Mill.; GC-MS; H9C2; ROS; boiled-egg model; mitochondrial membrane potential; nuclear condensation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Neurotrophic Effects of Foeniculum vulgare Ethanol Extracts on Hippocampal Neurons: Role of Anethole in Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptic Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 26;25(23):12701. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312701. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684414 Free PMC article.
-
Foeniculum vulgare Mill. increases cytosolic Ca2+ concentration and inhibits store-operated Ca2+ entry in vascular endothelial cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;84:800-805. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.10.013. Epub 2016 Oct 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27721178
-
Protective effect of fennel, and its major component trans-anethole against social isolation induced behavioral deficits in rats.Physiol Int. 2020 Mar;107(1):30-39. doi: 10.1556/2060.2020.00012. Physiol Int. 2020. PMID: 32491286
-
Exploring fennel (Foeniculum vulgare): Composition, functional properties, potential health benefits, and safety.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024;64(20):6924-6941. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2176817. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 36803269 Review.
-
Genetics, genomics and breeding of fennel.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 May 7;25(1):595. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06608-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40335931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multivalent Neuroprotective Activity of Elettaria cardamomum (Cardamom) and Foeniculum vulgare (Fennel) in H2O2-Induced Oxidative Stress in SH-SY5Y Cells and Acellular Assays.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;18(1):2. doi: 10.3390/ph18010002. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39861065 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophic Effects of Foeniculum vulgare Ethanol Extracts on Hippocampal Neurons: Role of Anethole in Neurite Outgrowth and Synaptic Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 26;25(23):12701. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312701. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684414 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

