Redox Homeostasis and Molecular Biomarkers in Precision Therapy for Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 39456418
- PMCID: PMC11504313
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101163
Redox Homeostasis and Molecular Biomarkers in Precision Therapy for Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
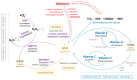
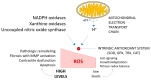
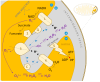
Precision medicine is envisioned as the future of cardiovascular healthcare, offering a more tailored and effective method for managing cardiovascular diseases compared to the traditional one-size-fits-all approaches. The complex role of oxidative stress in chronic diseases within the framework of precision medicine was carefully explored, delving into the cellular redox status and its critical involvement in the pathophysiological complexity of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The review outlines the mechanisms of reactive oxygen species generation and the function of antioxidants in maintaining redox balance. It emphasizes the elevated reactive oxygen species concentrations observed in heart failure and their detrimental impact on cardiovascular health. Various sources of ROS within the cardiovascular system are examined, including mitochondrial dysfunction, which contributes to oxidative stress and mitochondrial DNA degradation. The article also addresses oxidative stress's role in myocardial remodeling, a process pivotal to the progression of heart diseases. By integrating these aspects, the review underscores the importance of redox homeostasis and identifies molecular biomarkers that can enhance precision therapy for CVDs. The insights provided aim to pave the way for targeted therapeutic strategies that mitigate oxidative stress, thereby improving patient outcomes in cardiovascular medicine.
Keywords: cardiovascular system; heart failure; mitochondrial dysfunction; oxidative stress; precision medicine; redox homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deciphering Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Disease Progression: A Blueprint for Mechanistic Understanding and Therapeutic Innovation.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Dec 31;14(1):38. doi: 10.3390/antiox14010038. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39857372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Cardiac Diseases: Insights into Pathophysiology and Clinical Outcomes.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025 May 6. doi: 10.2174/011573403X379197250417061904. Online ahead of print. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2025. PMID: 40329726
-
Oxidative stress's impact on red blood cells: Unveiling implications for health and disease.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 1;103(9):e37360. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037360. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38428906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin and oxidative stress in cardiac pathology.Front Physiol. 2025 Feb 18;16:1550647. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1550647. eCollection 2025. Front Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40041164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moderate-Intensity Exercise Maintains Redox Homeostasis for Cardiovascular Health.Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023 Apr;7(4):e2200204. doi: 10.1002/adbi.202200204. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Adv Biol (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36683183 Review.
Cited by
-
The Janus Face of Oxidative Stress and Hydrogen Sulfide: Insights into Neurodegenerative Disease Pathogenesis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 19;14(3):360. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030360. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Soil to Brain: Olive Oil Attributes, Consumer Choices, Intermittent Fasting, and Their Impact on Health.Nutrients. 2025 Jun 1;17(11):1905. doi: 10.3390/nu17111905. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40507174 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α in high glucose-induced cardiac fibroblasts proliferation.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;16:1539690. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1539690. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39950114 Free PMC article.
-
L-Arginine and Nitric Oxide in Vascular Regulation-Experimental Findings in the Context of Blood Donation.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 13;17(4):665. doi: 10.3390/nu17040665. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40004994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in ARDS: mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 26;16:1603287. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1603287. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40642004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steven S., Frenis K., Oelze M., Kalinovic S., Kuntic M., Jimenez M.T.B., Vujacic-Mirski K., Helmstädter J., Kröller-Schön S., Münzel T., et al. Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019;2019:7092151. doi: 10.1155/2019/7092151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

