Metabolomic Profiling Reveals That Exercise Lowers Biomarkers of Cardiac Dysfunction in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes
- PMID: 39456421
- PMCID: PMC11505272
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101167
Metabolomic Profiling Reveals That Exercise Lowers Biomarkers of Cardiac Dysfunction in Rats with Type 2 Diabetes
Abstract
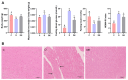
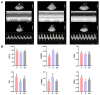
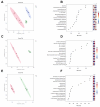
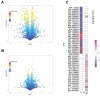
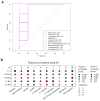
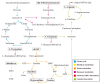
The increasing prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) leads to significant global health challenges, including cardiac structural and functional deficits, which in severe cases can progress to heart failure that can further strain healthcare resources. Aerobic exercise can ameliorate cardiac dysfunction in individuals with diabetes, although a comprehensive understanding of its underlying mechanisms remains elusive. This study utilizes untargeted metabolomics to reveal aerobic-exercise-activated metabolic biomarkers in the cardiac tissues of Sprague Dawley rats with T2DM. Metabolomics analysis revealed that diabetes altered 1029 myocardial metabolites, while aerobic exercise reversed 208 of these metabolites, of which 112 were upregulated and 96 downregulated. Pathway topology analysis suggested that these metabolites predominantly contributed to purine metabolism and arginine biosynthesis. Furthermore, receiver operating characteristic curve analysis identified 10 potential biomarkers, including xanthine, hypoxanthine, inosine, dGMP, l-glutamic acid, l-arginine, l-tryptophan, (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid, riboflavin, and glucolepidiin. Finally, data from Pearson correlation analysis indicated that some metabolic biomarkers strongly correlated with cardiac function. Our data suggest that certain metabolic biomarkers play an important role in ameliorating diabetes-related cardiac dysfunction by aerobic exercise.
Keywords: aerobic exercise; cardiac function; metabolomics; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the other authors reported any conflicts of interest in this study. The results of the study are presented clearly and honestly without fabrication, falsification, or inappropriate manipulation of data.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Untargeted Metabolomic Profiling Reveals Differentially Expressed Serum Metabolites and Pathways in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Cognitive Decline: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 13;25(4):2247. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042247. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38396924 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics reveals dynamic changes in metabolic profiles of rat supraspinatus tendon at three different time points after diabetes induction.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Nov 20;14:1292103. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1292103. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38053726 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Reveals Early Biomarkers in STZ-Induced Diabetic Rats With Cognitive Impairment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 30;12:665309. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.665309. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34276557 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated 16S rRNA Sequencing and Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis to Reveal the Protective Mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharide on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Model Rats.Curr Drug Metab. 2023;24(4):270-282. doi: 10.2174/1389200224666230406114012. Curr Drug Metab. 2023. PMID: 37038712
-
Serum Untargeted Metabolomics Reveal Potential Biomarkers of Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy in Asians.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 9;9:871291. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.871291. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35755823 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

