Antidiabetic and Antigout Properties of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Total Biflavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii Revealed by In Vitro and In Silico Studies
- PMID: 39456438
- PMCID: PMC11504096
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101184
Antidiabetic and Antigout Properties of the Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Total Biflavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii Revealed by In Vitro and In Silico Studies
Abstract
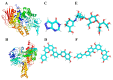
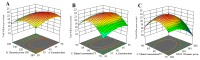
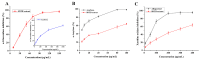
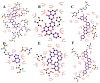
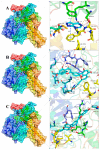
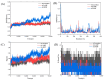
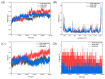
In this study, the extraction, purification and metabolic enzyme inhibition potential of Selaginella doederleinii were investigated. In order to extract the total biflavonoids from S. doederleinii (SDTBs), the optimum extraction process was obtained by optimizing the ultrasonic extraction parameters using response-surface methodology. This resulted in a total biflavonoid content of 22.26 ± 0.35 mg/g. Purification of the S. doederleinii extract was carried out using octadecylsilane (ODS), and the transfer rate of the SDTBs was 82.12 ± 3.48% under the optimum purification conditions. We determined the effect of the SDTBs on α-glucosidase (AG), α-amylase and xanthine oxidase (XOD) and found that the SDTBs had an extremely potent inhibitory effect on AG, with an IC50 value of 57.46 μg/mL, which was much lower than that of the positive control. Meanwhile, they also showed significant inhibition of XOD and α-amylase, with IC50 values of 289.67 μg/mL and 50.85 μg/mL, respectively. In addition, molecular docking studies were carried out to understand the nature of the action of the biflavonoids on AG and XOD. The results showed that robustaflavone had the lowest binding energy to AG (-11.33 kcal/mol) and XOD (-10.21 kcal/mol), while, on the other hand, amentoflavone showed a good binding affinity to AG (-10.40 kcal/mol) and XOD (-9.962 kcal/mol). Moreover, molecular dynamics simulations verified the above results.
Keywords: Selaginella doederleinii; bioflavonoids; enzyme inhibition; molecular docking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Wang S., Wan D., Liu W., Kang X., Zhou X., Sefidkon F., Hosseini M.M.Z., Zhang T., Pan X., Yang X. A Biflavonoid-Rich Extract from Selaginella doederleinii Hieron. against Throat Carcinoma via Akt/Bad and IKKβ/NF-κB/COX-2 Pathways. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15:1505. doi: 10.3390/ph15121505. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen M., Wang S., Cheng H., Wan D., Lu R., Yang X. Seladoeflavones G-I, Three New Flavonoids from Selaginella doederleinii Hieron. ChemistrySelect. 2022;7:e202202242. doi: 10.1002/slct.202202242. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

