Effects of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota Imbalance in Linwu Ducks
- PMID: 39456444
- PMCID: PMC11504935
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101190
Effects of Ferulic Acid on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Gut Microbiota Imbalance in Linwu Ducks
Abstract
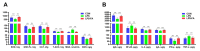
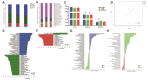
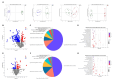
Oxidative stress is a major factor that limits the development of the poultry industry. Ferulic acid (FA) has an antioxidant effect in birds, but the mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, we stimulated oxidative stress in 28-day-old female Linwu ducks by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and fed them a diet supplemented with FA for 28 days. Results showed that FA alleviated LPS-induced growth performance regression, oxidative stress, and microbiota imbalance in ducks. An integrated metagenomics and metabolomics analysis revealed that s_Blautia_obeum, s_Faecalibacterium_prausnitzii, s_gemmiger_formicilis, and s_Ruminococcaceae_bacterium could be the biomarkers in the antioxidant effect of FA, which interacted with dihydro-3-coumaric acid, L-phenylalanine, and 13(S)-HODE, and regulated the phenylalanine metabolism and PPAR signaling pathway. This study revealed the mechanism of the antioxidant effect of FA, which provided evidence of applying FA as a new antioxidant in commercial duck production.
Keywords: Linwu duck; PPAR signaling pathway; antioxidant; ferulic acid; intestinal microbiota; metabolomics; metagenomics; phenylalanine metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Nawaz A.H., Amoah K., Leng Q.Y., Zheng J.H., Zhang W.L., Zhang L. Poultry response to heat stress: Its physiological, metabolic, and genetic implications on meat production and quality including strategies to improve broiler production in a warming world. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021;8:699081. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.699081. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kochish I.I., Titov V.Y., Nikonov I.N., Brazhnik E.A., Vorobyov N.I., Korenyuga M.V., Myasnikova O.V., Dolgorukova A.M., Griffin D.K., Romanov M.N. Unraveling signatures of chicken genetic diversity and divergent selection in breed-specific patterns of early myogenesis, nitric oxide metabolism and post-hatch growth. Front. Genet. 2023;13:1092242. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1092242. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

