Local Application of a New Chalconic Derivative (Chalcone T4) Reduces Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Periodontitis Model in Rats
- PMID: 39456446
- PMCID: PMC11504102
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101192
Local Application of a New Chalconic Derivative (Chalcone T4) Reduces Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Periodontitis Model in Rats
Abstract
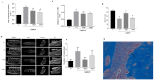
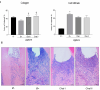
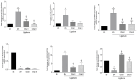
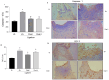
Chalcones are phenolic compounds with biological properties. This study had the aim to evaluate the effects of topical administration of a new synthetic chalcone, Chalcone T4, in an animal model of periodontitis induced by ligature. Forty rats were distributed in the following experimental groups: negative control (without periodontitis and topical application of distilled water), positive control (periodontitis and topical application of distilled water), chalcone I and II (periodontitis and topical application of 0.6 mg/mL and 1.8 mg/mL, respectively). Chalcone or distilled water was administered into the gingival sulcus of the first molars daily for 10 days, starting with the ligature installation. The following outcomes were evaluated: alveolar bone loss (µCT and methylene blue dye staining), quantification of osteoclasts (histomorphometry), cell infiltrate and collagen content (stereometry), gene expression of mediators (Nfact11, Tnf-α, Mmp-13, iNos, Sod and Nrf2) by (RT-qPCR); expression of BCL-2 and Caspase-1 (immunohistochemistry). Chalcone T4 inhibited bone resorption and prevented collagen matrix degradation. Reduction in the expression of inflammatory markers (Nfact11, Tnf-α, Mmp-13, and Caspase-1), attenuation of oxidative stress (iNOS reduction, and increase in Sod), and pro-apoptotic effect of the compound (BCL-2 reduction), were associated its effects on periodontal tissues. Topical application of Chalcone T4 prevented bone resorption and inflammation, demonstrating potential in the adjunctive treatment of periodontitis.
Keywords: antioxidant activity; chalcone; periodontitis; topical application.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander M.B., Damoulis P.D. The role of cytokines in the pathogenesis of periodontal disease. Curr. Opin. Periodontol. 1994:39–53. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

