Synthesis and Biological Activity Assessment of 2-Styrylbenzothiazoles as Potential Multifunctional Therapeutic Agents
- PMID: 39456450
- PMCID: PMC11504387
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101196
Synthesis and Biological Activity Assessment of 2-Styrylbenzothiazoles as Potential Multifunctional Therapeutic Agents
Abstract
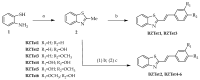
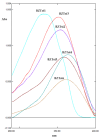
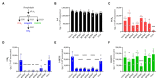
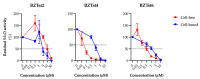
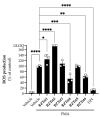
A current trend in healthcare research is to discover multifunctional compounds, able to interact with multiple biological targets, in order to simplify multi-drug therapies and improve patient compliance. The aim of this work was to outline the growing demand for innovative multifunctional compounds, achieved through the synthesis, characterisation and SAR evaluation of a series of 2-styrylbenzothiazole derivatives. The six synthesised compounds were studied for their potential as photoprotective, antioxidant, antiproliferative, and anti-inflammatory agents. In order to profile antioxidant activity against various radical species, in vitro DPPH, FRAP and ORAC assays were performed. UV-filtering activity was studied, first in solution and then in formulation (standard O/W sunscreen containing 3% synthesised molecules) before and after irradiation. Compound BZTst6 proved to be photostable, suitable for broad-spectrum criteria, and is an excellent UVA filter. In terms of antioxidant activity, only compound BZTst4 can be considered a promising candidate, due to the potential of the catechol moiety. Both also showed exceptional inhibitory action against the pro-inflammatory enzyme 5-lipoxygenase (LO), with IC50 values in the sub-micromolar range in both activated neutrophils and under cell-free conditions. The results showed that the compounds under investigation are suitable for multifunctional application purposes, underlining the importance of their chemical scaffolding in terms of different biological behaviours.
Keywords: ant-inflammatory; antioxidants; antitumor; benzothiazole derivatives; multifunctional.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Duarte C.W., Vaughan L.K., Mark Beasley T., Tiwari H.K. Biomedical Sciences. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2014. Multifactorial Inheritance and Complex Diseases Reference Module.
-
- Storr T. Multifunctional compounds for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Can. J. Chem. 2021;99:1–9. doi: 10.1139/cjc-2020-0279. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

