The Effect of Multilayer Nanoemulsion on the In Vitro Digestion and Antioxidant Activity of β-Carotene
- PMID: 39456471
- PMCID: PMC11504132
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101218
The Effect of Multilayer Nanoemulsion on the In Vitro Digestion and Antioxidant Activity of β-Carotene
Abstract
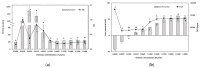
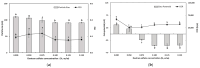
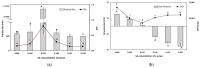
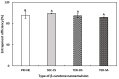
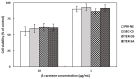
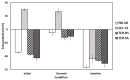
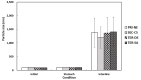
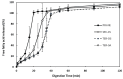
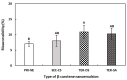
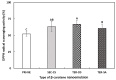
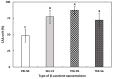
The objectives of this study were to design multilayer oil-in-water nanoemulsions using a layer-by-layer technique to enhance the stability of β-carotene and evaluate its effect on in vitro release and antioxidant activity. To prepare β-carotene-loaded multilayer nanoemulsions (NEs), a primary NE (PRI-NE) using Tween 20 was coated with chitosan (CS) for the secondary NE (SEC-CS), and with dextran sulfate (DS) and sodium alginate (SA) for the two types of tertiary NEs (TER-DS, TER-SA). The multilayer NEs ranged in particle size from 92 to 110 nm and exhibited high entrapment efficiency (92-99%). After incubation in a simulated gastrointestinal tract model, the release rate of free fatty acids decreased slightly after coating with CS, DS, and SA. The bioaccessibility of β-carotene was 7.02% for the PRI-NE, 7.96% for the SEC-CS, 10.88% for the TER-DS, and 10.25% for the TER-SA. The 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging abilities increased by 1.2 times for the multilayer NEs compared to the PRI-NE. In addition, the cellular antioxidant abilities improved by 1.8 times for the TER-DS (87.24%) compared to the PRI-NE (48.36%). Therefore, multilayer nanoemulsions are potentially valuable techniques to improve the stability, in vitro digestion, and antioxidant activity of β-carotene.
Keywords: antioxidant; in vitro digestion; multilayer nanoemulsions; β-carotene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sheng B., Li L., Zhang X., Jiao W., Zhao D., Wang X., Wan L., Li B., Rong H. Physicochemical properties and chemical stability of β-carotene bilayer emulsion coated with bovine serum albumin and Arabic gum compared to monolayer emulsions. Molecules. 2018;23:495. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020495. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodríduez-Huezo M., Pedroza-Islas R., Prado-Barragán L., Beristain C., Vernon-Carter E. Microencapsulation by spray drying of multiple emulsions containing carotenoids. J. Food Sci. 2004;69:351–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2004.tb13641.x. - DOI
-
- Rodriguez-Amaya D.B. Food Carotenoids: Chemistry, Biology and Technology. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2015.
-
- Mao L., Xu D., Yang J., Yuan F., Gao Y., Zhao J. Effects of small and large molecule emulsifiers on the characteristics of β-carotene nanoemulsions prepared by high pressure homogenization. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2009;47:336–342.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

