Dietary Polyphenols, Food Processing and Gut Microbiome: Recent Findings on Bioavailability, Bioactivity, and Gut Microbiome Interplay
- PMID: 39456473
- PMCID: PMC11505337
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101220
Dietary Polyphenols, Food Processing and Gut Microbiome: Recent Findings on Bioavailability, Bioactivity, and Gut Microbiome Interplay
Abstract
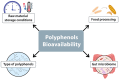
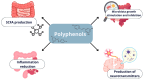
Polyphenols are organic chemical compounds naturally present in plants, renowned for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, anticancer, and cardiovascular protective properties. Their bioactivity and bioavailability can vary widely depending on the methods of food processing and interactions with the gut microbiome. These factors can induce changes in polyphenols, affecting their ability to achieve their intended health benefits. Thus, it is essential to develop and apply food processing methods that optimize polyphenol content while maintaining their bioactivity and bioavailability. This review aims to explore how various food processing techniques affect the quantity, bioactivity, and bioavailability of polyphenols, as well as their interactions with the gut microbiome, which may ultimately determine their health effects.
Keywords: bioactivity; bioavailability; food processing; microbiome; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ifie I., Marshall L.J. Food Processing and Its Impact on Phenolic Constituents in Food. Cogent Food Agric. 2018;4:1507782. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2018.1507782. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources