Unraveling Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Involvement in Psoriasis: The Promise of Antioxidant Therapies
- PMID: 39456475
- PMCID: PMC11505169
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101222
Unraveling Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Involvement in Psoriasis: The Promise of Antioxidant Therapies
Abstract
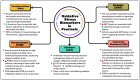
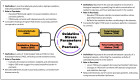
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by immune dysregulation and aberrant keratinocyte proliferation. Despite tremendous advances in understanding its etiology, effective therapies that target its fundamental mechanisms remain necessary. Recent research highlights the role of reactive oxygen species dysregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction in psoriasis pathogenesis. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species mediate cellular signaling pathways involved in psoriasis, such as proliferation, apoptosis, and inflammation, leading to oxidative stress, exacerbating inflammation and tissue damage if dysregulated. This review explores oxidative stress biomarkers and parameters in psoriasis, including myeloperoxidase, paraoxonase, sirtuins, superoxide dismutase, catalase, malondialdehyde, oxidative stress index, total oxidant status, and total antioxidant status. These markers provide insights into disease mechanisms and potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Modulating mitochondrial reactive oxygen species levels and enhancing antioxidant defenses can alleviate inflammation and oxidative damage, improving patient outcomes. Natural antioxidants like quercetin, curcumin, gingerol, resveratrol, and other antioxidants show promise as complementary treatments targeting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. This review aims to guide the development of personalized therapeutic methods and diagnostic techniques, emphasizing the importance of comprehensive clinical studies to validate the efficacy and safety of these interventions, paving the way for more effective and holistic psoriasis care.
Keywords: antioxidant; mitochondrial dysfunction; mitochondrial reactive oxygen species; natural products; oxidative stress; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidative Imbalance in Psoriasis with an Emphasis on Psoriatic Arthritis: Therapeutic Antioxidant Targets.Molecules. 2024 Nov 19;29(22):5460. doi: 10.3390/molecules29225460. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39598849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial biogenesis: pharmacological approaches.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(35):5507-9. doi: 10.2174/138161282035140911142118. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 24606795
-
Role of oxidative stress in various stages of psoriasis.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2010 Oct;25(4):388-92. doi: 10.1007/s12291-010-0043-9. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2010. PMID: 21966111 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress involvement in psoriasis: a systematic review.Free Radic Res. 2019 Aug;53(8):829-840. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2019.1648800. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Free Radic Res. 2019. PMID: 31392915
-
Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in otorhinolaryngological diseases: insights from pathophysiology to targeted antioxidant therapies.Redox Rep. 2025 Dec;30(1):2458942. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2025.2458942. Epub 2025 Feb 2. Redox Rep. 2025. PMID: 39894944 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Photodynamically tunable ROS-generating hydrogels for accelerated tissue regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jul 8;51:977-992. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.05.006. eCollection 2025 Sep. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40688654 Free PMC article.
-
Astilbin Alleviates IL-17-Induced Hyperproliferation and Inflammation in HaCaT Cells via Inhibiting Ferroptosis Through the cGAS-STING Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 24;26(11):5075. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115075. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40507886 Free PMC article.
-
JNK/c-Jun cascade activation enhances malignant proliferation of psoriatic keratinocytes by regulating ROS levels and mitochondrial membrane potential.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Aug 18;30(1):754. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02912-w. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40826129 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Damiani G., Bragazzi N.L., Karimkhani Aksut C., Wu D., Alicandro G., McGonagle D., Guo C., Dellavalle R., Grada A., Wong P., et al. The Global, Regional, and National Burden of Psoriasis: Results and Insights from the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Study. Front. Med. 2021;8:743180. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.743180. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

