Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Biological Mechanisms and Health Benefits
- PMID: 39456481
- PMCID: PMC11505271
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101228
Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Biological Mechanisms and Health Benefits
Abstract
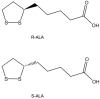
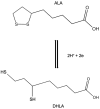
Alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) is a bioactive molecule with significant health effects. The biological action of ALA has been ascribed to the characteristic antioxidant properties of the oxidized form (ALA) and its reduced counterpart the dihydrolipoic acid (DHLA) system. The ALA/DHLA combination represents an ideal antioxidant since it can quench radicals, is able to chelate metals, is amphiphilic, and has no major adverse effects. This unique system is able to scavenge reactive oxygen species, exerting a major effect on tissue levels of reduced forms of other antioxidants, including glutathione. For this reason, ALA is also known as the "antioxidant of antioxidants". This review analyzes the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects of ALA and discusses its applications as an ameliorative tool for chronic diseases and those associated with oxidative stress. Results from in vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that ALA modulates various oxidative stress pathways suggesting its application, alone or in combination with other functional substances, as a useful support in numerous conditions, in which the balance oxidant-antioxidant is disrupted, such as neurodegenerative disorders. Based on several successful clinical studies, it has been also established that oral ALA supplements are clinically useful in relieving the complications of diabetes and other disorders including cardiovascular diseases and nerve discomforts suggesting that ALA can be considered a useful approach to improving our health.
Keywords: alpha-lipoic acid; anti-inflammatory activity; antioxidant activity; food supplement; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
Rosario Russo was employed by the company Giellepi S.p.A. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The pharmacology of the antioxidant lipoic acid.Gen Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;29(3):315-31. doi: 10.1016/s0306-3623(96)00474-0. Gen Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9378235 Review.
-
Antioxidant properties of an endogenous thiol: Alpha-lipoic acid, useful in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Nov;54(5):391-8. doi: 10.1097/fjc.0b013e3181be7554. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19998523 Review.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid and cardiovascular disease.J Nutr. 2003 Nov;133(11):3327-30. doi: 10.1093/jn/133.11.3327. J Nutr. 2003. PMID: 14608040 Review.
-
[An endogenous dithiol with antioxidant properties: alpha-lipoic acid, potential uses in cardiovascular diseases].Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2008 Jun;57(3):161-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ancard.2008.02.018. Epub 2008 Jun 4. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18571145 Review. French.
-
Benefits of α-lipoic acid in high-risk pregnancies (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2021 Nov;22(5):1232. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10666. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34539828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Alpha-Lipoic Acid: Unraveling Its Role in Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Conditions.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 30;47(5):322. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050322. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary and Nutritional Interventions for the Management of Endometriosis.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 21;16(23):3988. doi: 10.3390/nu16233988. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39683382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of a Formulation Containing Chaga Extract, Coenzyme Q10, and Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress: NMR Metabolomic Insights into Cellular Energy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jun 18;14(6):753. doi: 10.3390/antiox14060753. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40563385 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-lipoic acid alleviates oxidative stress and brain damage in patients with sevoflurane anesthesia.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Mar 20;16:1572156. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1572156. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40183089 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-Lipoic Acid Alleviates Lead-Induced Testicular Damage in Roosters by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Modulating Key Pathways.Toxics. 2025 Apr 25;13(5):341. doi: 10.3390/toxics13050341. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40423420 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Satoh S., Shindoh M., Min J.Z., Toyo’oka T., Fukushima T., Inagaki S. Selective and sensitive determination of lipoyllysine (protein-bound alpha-lipoic acid) in biological specimens by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2008;618:210–217. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

