Comparative Study of an Antioxidant Compound and Ethoxyquin on Feed Oxidative Stability and on Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Health in Starter Broiler Chickens
- PMID: 39456482
- PMCID: PMC11505240
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101229
Comparative Study of an Antioxidant Compound and Ethoxyquin on Feed Oxidative Stability and on Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, and Intestinal Health in Starter Broiler Chickens
Abstract
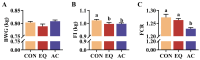
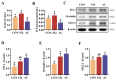
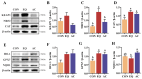
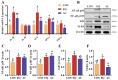
Concerns over the safety of ethoxyquin (EQ) highlight the need for safer, more effective feed antioxidants. This study investigated a healthier antioxidant compound (AC) as a potential alternative to EQ in broilers. A total of 351 one-day-old Arbor Acres Plus male broilers were randomly assigned to three treatments for 21 days: control (CON), EQ group (200 g/ton EQ at 60% purity), and AC group (200 g/ton AC containing 18% butylated hydroxytoluene, 3% citric acid, and 1% tertiary butylhydroquinone). AC supplementation reduced the acid value, peroxide value, and malondialdehyde content in stored feed, decreased feed intake and the feed conversion ratio without affecting body weight gain, and enhanced antioxidant capacity (liver total antioxidant capacity and superoxide dismutase; intestinal catalase and glutathione peroxidase 7). It improved intestinal morphology and decreased barrier permeability (lower diamine oxidase and D-lactate), potentially by promoting ZO-1, Occludin, and Mucin2 expression. The AC also upregulated NF-κB p50 and its inhibitor (NF-κB p105), enhancing immune regulation. Additionally, the AC tended to increase beneficial gut microbiota, including Lactobacillus, and reduced Bacteroides, Corprococcus, and Anaeroplasma. Compared to EQ, the AC further enhanced feed oxidative stability, the feed conversion ratio, intestinal morphology and barrier functions, and inflammatory status, suggesting its potential as a superior alternative to EQ for broiler diets.
Keywords: antioxidant capacity; antioxidant compound; broiler; ethoxyquin; intestinal health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

