Nannochloropsis oceanica Lipid Extract Moderates UVB-Irradiated Psoriatic Keratinocytes: Impact on Protein Expression and Protein Adducts
- PMID: 39456489
- PMCID: PMC11504445
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101236
Nannochloropsis oceanica Lipid Extract Moderates UVB-Irradiated Psoriatic Keratinocytes: Impact on Protein Expression and Protein Adducts
Abstract
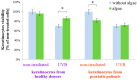
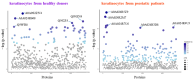
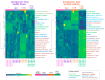
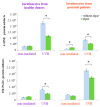
Psoriasis is characterized by excessive exfoliation of the epidermal layer due to enhanced pro-inflammatory signaling and hyperproliferation of keratinocytes, further modulated by UV-based anti-psoriatic treatments. Consequently, this study aimed to evaluate the impact of a lipid extract derived from the microalgae Nannochloropsis oceanica on the proteomic alterations induced by lipid derivatives in non-irradiated and UVB-irradiated keratinocytes from psoriatic skin lesions compared to keratinocytes from healthy individuals. The findings revealed that the microalgae extract diminished the viability of psoriatic keratinocytes without affecting the viability of these cells following UVB exposure. Notably, the microalgae extract led to an increased level of 4-HNE-protein adducts in non-irradiated cells and a reduction in 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE)-protein and 15-deoxy-12,14-prostaglandin J2 (15d-PGJ2)-protein adducts in UVB-exposed keratinocytes from psoriasis patients. In healthy skin cells, the extract decreased the UV-induced elevation of 4-HNE-protein and 15d-PGJ2-protein adducts. The antioxidant/anti-inflammatory attributes of the lipid extract from the Nannochloropsis oceanica suggest its potential as a protective agent for keratinocytes in healthy skin against UVB radiation's detrimental effects. Moreover, it could offer therapeutic benefits to skin cells afflicted with psoriatic lesions by mitigating their proliferation and inflammatory responses during UV radiation treatment.
Keywords: UVB radiation; keratinocytes; lipid extract; microalgae Nannochloropsis oceanica; protein adducts; psoriasis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Report on Psoriasis. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

