Innovations in Nuclear Medicine Imaging for Reactive Oxygen Species: Applications and Radiopharmaceuticals
- PMID: 39456507
- PMCID: PMC11504556
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox13101254
Innovations in Nuclear Medicine Imaging for Reactive Oxygen Species: Applications and Radiopharmaceuticals
Abstract
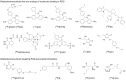
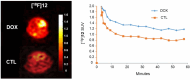
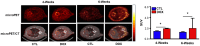
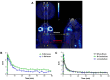
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated during normal cellular energy production and play a critical role in maintaining cellular function. However, excessive ROS can damage cells and tissues, contributing to the development of diseases such as cardiovascular, inflammatory, and neurodegenerative disorders. This review explores the potential of nuclear medicine imaging techniques for detecting ROS and evaluates various radiopharmaceuticals used in these applications. Radiopharmaceuticals, which are drugs labeled with radionuclides, can bind to specific biomarkers, facilitating their identification in vivo using nuclear medicine equipment, i.e., positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography, for diagnostic purposes. This review includes a comprehensive search of PubMed, covering radiopharmaceuticals such as analogs of fluorescent probes and antioxidant vitamin C, and biomarkers targeting mitochondrial complex I or cystine/glutamate transporter.
Keywords: nuclear medicine; oxidative stress; positron emission tomography; radiopharmaceutical; reactive oxygen species; single photon emission computed tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
We (B.S.M. and B.S.K.), as the corresponding authors, declare on behalf of all the authors of the submission that there is not any financial interest or personal relationship with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence this work. This submission has been approved by all coauthors, and all authors fully endorse the contents of this report.
Figures
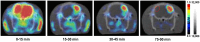

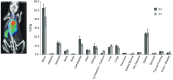




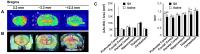

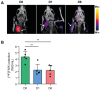

References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

