Overcoming Irinotecan Resistance by Targeting Its Downstream Signaling Pathways in Colon Cancer
- PMID: 39456585
- PMCID: PMC11505920
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16203491
Overcoming Irinotecan Resistance by Targeting Its Downstream Signaling Pathways in Colon Cancer
Abstract
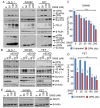
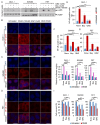
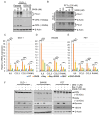
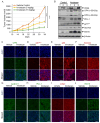
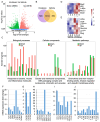
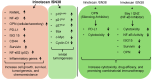
Among the most popular chemotherapeutic agents, irinotecan, regarded as a prodrug belonging to the camptothecin family that inhibits topoisomerase I, is widely used to treat metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). Although immunotherapy is promising for several cancer types, only microsatellite-instable (~7%) and not microsatellite-stable CRCs are responsive to it. Therefore, it is important to investigate the mechanism of irinotecan function to identify cellular proteins and/or pathways that could be targeted for combination therapy. Here, we have determined the effect of irinotecan treatment on the expression/activation of tumor suppressor genes (including p15Ink4b, p21Cip1, p27Kip1, and p53) and oncogenes (including OPN, IL8, PD-L1, NF-κB, ISG15, Cyclin D1, and c-Myc) using qRT-PCR, Western blotting, immunofluorescence (IF), and RNA sequencing of tumor specimens. We employed stable knockdown, neutralizing antibodies (Abs), and inhibitors of OPN, p53, and NF-κB to establish downstream signaling and sensitivity/resistance to the cytotoxic activities of irinotecan. Suppression of secretory OPN and NF-κB sensitized colon cancer cells to irinotecan. p53 inhibition or knockdown was not sufficient to block or potentiate SN38-regulated signaling, suggesting p53-independent effects. Irinotecan treatment inhibited tumor growth in syngeneic mice. Analyses of allograft tumors from irinotecan-treated mice validated the cell culture results. RNA-seq data suggested that irinotecan-mediated activation of NF-κB signaling modulated immune and inflammatory genes in mice, which may compromise drug efficacy and promote resistance. In sum, these results suggest that, for CRCs, targeting OPN, NF-κB, PD-L1, and/or ISG15 signaling may provide a potential strategy to overcome resistance to irinotecan-based chemotherapy.
Keywords: CDKIs; ISG15; NF-κB; PD-L1; SN38; colorectal cancer; drug resistance; immunomodulation; irinotecan; osteopontin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cremolini C., Casagrande M., Loupakis F., Aprile G., Bergamo F., Masi G., Moretto R., Pietrantonio F., Marmorino F., Zucchelli G., et al. Efficacy of FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab in liver-limited metastatic colorectal cancer: A pooled analysis of clinical studies by Gruppo Oncologico del Nord Ovest. Eur. J. Cancer. 2017;73:74–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.10.028. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

