B Cell Lymphoma 6 (BCL6): A Conserved Regulator of Immunity and Beyond
- PMID: 39456751
- PMCID: PMC11507070
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252010968
B Cell Lymphoma 6 (BCL6): A Conserved Regulator of Immunity and Beyond
Abstract
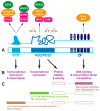
B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is a conserved multi-domain protein that functions principally as a transcriptional repressor. This protein regulates many pivotal aspects of immune cell development and function. BCL6 is critical for germinal center (GC) formation and the development of high-affinity antibodies, with key roles in the generation and function of GC B cells, follicular helper T (Tfh) cells, follicular regulatory T (Tfr) cells, and various immune memory cells. BCL6 also controls macrophage production and function as well as performing a myriad of additional roles outside of the immune system. Many of these regulatory functions are conserved throughout evolution. The BCL6 gene is also important in human oncology, particularly in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and follicular lymphoma (FL), but also extending to many in other cancers, including a unique role in resistance to a variety of therapies, which collectively make BCL6 inhibitors highly sought-after.
Keywords: B cell; BCL6; T cell; cancer; germinal center; lymphoma; macrophage; repressor; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

