Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR), Growth Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15), and Soluble C5b-9 (sC5b-9) Levels Are Significantly Associated with Endothelial Injury Indices in CAR-T Cell Recipients
- PMID: 39456810
- PMCID: PMC11507105
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011028
Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (suPAR), Growth Differentiation Factor-15 (GDF-15), and Soluble C5b-9 (sC5b-9) Levels Are Significantly Associated with Endothelial Injury Indices in CAR-T Cell Recipients
Abstract
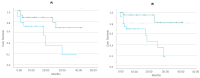
Endothelial injury indices, such as Endothelial Activation and Stress Index (EASIX), modified EASIX (m-EASIX), and simplified EASIX (s-EASIX) scores, have been previously associated with chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T) cell immunotherapy complications. Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR), growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), and soluble C5b-9 (sC5b-9) have been described as markers of endothelial injury post-hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In the current study, we examined whether suPAR, GDF-15, and sC5b-9 levels were associated with endothelial injury indices in adult CAR-T cell recipients. The levels of these markers were measured in patients before CAR-T cell infusion and in healthy individuals with immunoenzymatic methods. We studied 45 CAR-T cell recipients and 20 healthy individuals as the control group. SuPAR, GDF-15, and sC5b-9 levels were significantly higher in the patients' group compared to the healthy control group (p < 0.001, in all comparisons). SuPAR levels at baseline were associated with the m-EASIX scores calculated at the same time point (p = 0.020), while suPAR and GDF-15 concentrations were correlated with EASIX scores at day 14 post-infusion (p < 0.001 in both comparisons). Moreover, sC5b-9 levels were correlated with the s-EASIX scores at infusion (p = 0.008) and the EASIX scores at day 14 (p = 0.005). In our study, sC5b9, suPAR, and GDF-15 levels were found to reflect endothelial injury in CAR-T cell recipients.
Keywords: chimeric antigen receptor-T (CAR-T); complement; cytokine release syndrome (CRS); endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX); endothelial dysfunction; growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15); immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS); soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR).
Conflict of interest statement
E.G. has received honoraria or research funding from Astra Zeneca, Gilead, Jazz, Omeros, Sanofi, and Sobi. These companies had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. The remaining authors had no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lee D.W., Santomasso B.D., Locke F.L., Ghobadi A., Turtle C.J., Brudno J.N., Maus M.V., Park J.H., Mead E., Pavletic S., et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25:625–638. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.12.758. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rejeski K., Subklewe M., Aljurf M., Bachy E., Balduzzi A., Barba P., Bruno B., Benjamin R., Carrabba M.G., Chabannon C., et al. Immune Effector Cell–Associated Hematotoxicity: EHA/EBMT Consensus Grading and Best Practice Recommendations. Blood. 2023;142:865–877. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023020578. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

