Impaired Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation and Increased Levels of Soluble Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-1 Induced by Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure in Pregnant Rats: Evidence of Protective Effects with Sodium Nitrite Treatment in Preeclampsia
- PMID: 39456834
- PMCID: PMC11507509
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011051
Impaired Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation and Increased Levels of Soluble Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase-1 Induced by Reduced Uterine Perfusion Pressure in Pregnant Rats: Evidence of Protective Effects with Sodium Nitrite Treatment in Preeclampsia
Abstract
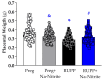
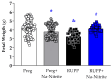
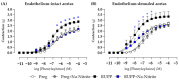
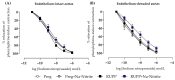
Preeclampsia (PE) is a hypertensive disorder of pregnancy and is associated with increases in soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 (sFlt-1) and reductions in nitric oxide (NO) levels. Placental ischemia and hypoxia are hypothesized as initial pathophysiological events of PE. Nitrite (NO metabolite) may be recycled back to NO in ischemic and hypoxic tissues. Therefore, this study examined the sodium nitrite effects in an experimental model of PE. Pregnant rats received saline (Preg group) or sodium nitrite (Preg + Na-Nitrite group). Pregnant rats submitted to the placental ischemia received saline (RUPP group) or sodium nitrite (RUPP + Na-Nitrite group). Blood pressure, placental and fetal weights, and the number of pups were recorded. Plasma levels of NO metabolites and sFlt-1 were also determined. Vascular and endothelial functions were also measured. Blood pressure, placental and fetal weights, the number of pups, NO metabolites, sFlt-1 levels, vascular contraction, and endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the RUPP + Na-Nitrite rats were brought to levels comparable to those in Preg rats. In conclusion, sodium nitrite may counteract the reductions in NO and increases in sFlt-1 levels induced by the placental ischemia model of PE, thus suggesting that increased blood pressure and vascular and endothelial dysfunctions may be attenuated by sodium nitrite-derived NO.
Keywords: endothelial dysfunction; nitric oxide; placental ischemia; preeclampsia; sodium nitrite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Poon L.C., Shennan A., Hyett J.A., Kapur A., Hadar E., Divakar H., McAuliffe F., da Silva Costa F., von Dadelszen P., McIntyre H.D., et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) initiative on pre-eclampsia: A pragmatic guide for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019;145:1–33. doi: 10.1002/ijgo.12802. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis E.F., Lazdam M., Lewandowski A.J., Worton S.A., Kelly B., Kenworthy Y., Adwani S., Wilkinson A.R., McCormick K., Sargent I., et al. Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Children and Young Adults Born to Preeclamptic Pregnancies: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics. 2012;129:e1552–e1561. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-3093. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

