Environmental Diagnosis through a Flow Cytometric Approach
- PMID: 39456852
- PMCID: PMC11507161
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011069
Environmental Diagnosis through a Flow Cytometric Approach
Abstract
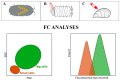
In an era when ecological and environmental needs and responsibilities apply pressure on the world's countries and sustainability takes centre stage, ecologic/environmental (E/E) laboratories stand as beacons of scientific inquiry, innovating, optimising, and applying various tests for a better knowledge of our natural resources and the quality status of ecosystems. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the use of flow cytometry (FC) as a tool for assessing environmental quality, mainly using living organisms and their biological changes as bioindicators. Cytometric approaches applied to both marine and terrestrial ecosystems ensure the detection of biochemical and functional status of the cells composing either an organ thereof or the organism itself. In addition to cytometric evaluations of the biotic matrix, a brief overview of the techniques for the environmental assessment of biotic and abiotic matrices using mass spectrometry is given. The technique involving the continuous monitoring of the chemical and physical parameters of water, sediment, and soil is basically incapable of detecting any additive and synergetic effects of toxicants on living organisms. Therefore, techniques employing bioindicators provide valuable information for environmental diagnosis, and several studies have demonstrated the strong relationship between specific environmental data and cell/organ behaviour.
Keywords: bioindicator; biomarker; haemolymph; hepatopancreas; marine; terrestrial.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Chowdhury S., Dubey V.K., Choudhury S., Das A., Jeengar D., Sujatha B., Kumar A., Kumar N., Semwal A., Kumar V. Insects as Bioindicator: A Hidden Gem for Environmental Monitoring. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023;11:1146052. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2023.1146052. - DOI
-
- Carter J.L., Resh V.H., Hannaford M.J. Methods in Stream Ecology. 3rd ed. Vol. 2. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2017. Macroinvertebrates as Biotic Indicators of Environmental Quality; pp. 293–318. - DOI
-
- Huang Y., Zeng Q., Xu W., Zhang D., Xiao J., Song H., Xiao F., Wang J., Xie W. Soil Meso- and Microfauna Community Acts as an Environmental Bioindicator in Urban Greenway Landscapes. Geoderma. 2024;442:116775. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2024.116775. - DOI
-
- Stenger L.R., Ferguson F.M., Skvarla M. Water Mites and Their Use as Bioindicators of Water Quality Conditions: A Pennsylvania Case Study. Acarologia. 2024;64:146–163. doi: 10.24349/qo5i-rvld. - DOI
-
- Markert B., Breure A.M., Zechmeister H.G. In: Bioindicators and Biomonitors. Principles, Concepts and Applications. Nriagu J.O., editor. Elsevier, Science Ltd.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2003. pp. 3–21.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

