Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy: Predictors of Response, Issues, and Challenges
- PMID: 39456872
- PMCID: PMC11507510
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011091
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy: Predictors of Response, Issues, and Challenges
Abstract
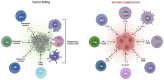
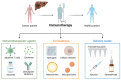
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as durvalumab, tremelimumab, and atezolizumab, have emerged as a significant therapeutic option for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In fact, the efficacy of ICIs as single agents or as part of combination therapies has been demonstrated in practice-changing phase III clinical trials. However, ICIs confront several difficulties, including the lack of predictive biomarkers, primary and secondary drug resistance, and treatment-related side effects. Herein, we provide an overview of current issues and future challenges in this setting.
Keywords: PD-L1; cancer; hepatocellular carcinoma; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immunotherapy; liver cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Benson A.B., D’Angelica M.I., Abbott D.E., Anaya D.A., Anders R., Are C., Bachini M., Borad M., Brown D., Burgoyne A., et al. Hepatobiliary Cancers, Version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021;19:541–565. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2021.0022. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ayuso C., Rimola J., Vilana R., Burrel M., Darnell A., García-Criado Á., Bianchi L., Belmonte E., Caparroz C., Barrufet M., et al. Diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Current guidelines. Eur. J. Radiol. 2018;101:72–81. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.01.025. Erratum in Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 112, 229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.01.018 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials