Biological Activity Evaluation of Phenolic Isatin-3-Hydrazones Containing a Quaternary Ammonium Center of Various Structures
- PMID: 39456912
- PMCID: PMC11507835
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms252011130
Biological Activity Evaluation of Phenolic Isatin-3-Hydrazones Containing a Quaternary Ammonium Center of Various Structures
Abstract
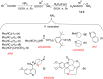
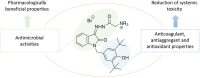
A series of new isatin-3-hydrazones bearing different ammonium fragments was synthesized by a simple and easy work-up reaction of Girard's reagents analogs with 1-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)isatin. All derivatives have been shown to have antioxidant properties. In terms of bactericidal activity against gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus, the best compounds are 3a, 3e, and 3m, bearing octyl, acetal, and brucine ammonium centers, respectively. In addition, brucine and quinine derivatives 3l, and 3j exhibit platelet antiaggregation activity at the level of acetylsalicylic acid, and this series of isatin derivatives does not adversely affect the hemostasis system as a whole. Thus, all the obtained results can lay the groundwork for future pharmaceutical developments for the creation of effective antibacterial drugs with reduced systemic toxicity due to the presence of antioxidant properties.
Keywords: antioxidants; cytotoxicity; hemostasis; hydrazones; isatin; quaternary ammonium compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Nurbol Appazov was employed by the company “CNEC” LLP. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

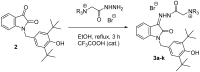


References
-
- Bharathi Dileepan A.G., Daniel Prakash T., Ganesh Kumar A., Shameela Rajam P., Violet Dhayabaran V., Rajaram R. Isatin based macrocyclic Schiff base ligands as novel candidates for antimicrobial and antioxidant drug design: In vitro DNA binding and biological studies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 2018;183:191–200. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.029. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

